« The social costs of the Industrial Revolution » : différence entre les versions
Aucun résumé des modifications |
|||
| Ligne 53 : | Ligne 53 : | ||
[[File:Vue de Verviers. Joseph Fussell (1818-1912).jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.1|View of Verviers (mid-19th c.)Watercolour by J. Fussell.]] | [[File:Vue de Verviers. Joseph Fussell (1818-1912).jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.1|View of Verviers (mid-19th c.)Watercolour by J. Fussell.]] | ||
The Industrial Revolution led to major migration from rural to urban areas, irreversibly transforming European societies. In the context of textile towns, this rural exodus was particularly pronounced. Craftsmen and proto-industrial workers, traditionally dispersed in the countryside where they worked at home or in small workshops, were forced to congregate in the industrial cities. This was due to the need to be close to the factories, as long journeys between home and work became impractical with the increasingly regulated work structure of the factory. The concentration of workers in cities had several consequences. On the one hand, the proximity of workers to production sites enabled more efficient management and rationalisation of the work process, leading to an explosion in productivity without necessarily increasing the number of workers employed. Indeed, innovations in production techniques, such as the use of steam engines and the automation of weaving and spinning processes, have considerably increased yields while maintaining or reducing the workforce required. In cities, the concentration of the population also led to rapid densification and urbanisation, as shown by the example of Verviers. The population of this Belgian textile town almost tripled over the course of the nineteenth century, rising from 35,000 at the start to 100,000 by the end of the century. This rapid expansion of the urban population often led to hasty urbanisation and difficult living conditions, as the existing infrastructure was rarely adequate to cope with such an influx. The concentration of the workforce also changed the social structure of cities, creating new classes of industrial workers and altering existing socio-economic dynamics. It also had an impact on the urban fabric, with the construction of housing for workers, the expansion of urban services and facilities, and the development of new forms of community life centred around the factory rather than the traditional structures of the city. Ultimately, the phenomenon of textile towns during the Industrial Revolution illustrates the transformative power of industrialisation on settlement patterns, the economy and society as a whole. | |||
The steel regions, often referred to as 'black countries' because of the soot and pollution from factories and mines, illustrate another facet of the impact of industrialisation on demography and urban development. The black countries were centred on the coal and iron industries, which were essential catalysts for the industrial revolution. The demographic explosion in these regions was due less to an increase in the number of workers per mine or factory than to the emergence of new labour-intensive industries. Although mechanisation was progressing, it was not yet replacing the need for workers in coal mines and ironworks. For example, although the steam engine made it possible to ventilate the galleries and increase the productivity of the mines, extracting coal was still a very laborious job requiring large numbers of workers. The demographic growth in towns such as Liège, where the population rose from 50,000 to 400,000, bears witness to this industrial expansion. The coalfields and steelworks became centres of attraction for workers looking for work, leading to rapid growth in the surrounding towns. These workers were often migrants from the countryside or other less industrialised regions, attracted by the job opportunities created by these new industries. These industrial towns grew at an impressive rate, often without the planning or infrastructure needed to adequately accommodate their new population. The result was precarious living conditions, with overcrowded and unhealthy housing, public health problems and growing social tensions. These challenges would eventually lead to urban and social reforms in the following centuries, but during the Industrial Revolution, these regions were marked by rapid and often chaotic transformation.[[Fichier:Développement démographique saint Etienne vs Roubaix.png|200px|vignette]] | |||
This graph shows the significant demographic growth of Saint-Étienne and Roubaix, two emblematic cities of the French industrial epic, over the period from 1811 to 1911. Over the course of the century, these towns saw their populations grow considerably as a result of rampant industrialisation. In Roubaix, the growth was particularly striking. Known for its flourishing textile industry, the town grew from fewer than 10,000 inhabitants at the start of the century to around 150,000 at its end. The labour-intensive textile industry led to a massive migration of rural populations to Roubaix, radically transforming its social and urban landscape. Saint-Étienne followed a similar upward curve, although its numbers remained lower than those of Roubaix. As a strategic centre for metallurgy and arms manufacture, the town also created a huge demand for skilled and unskilled workers, which contributed to its demographic boom. Industrialisation was the catalyst for a major social change, reflected in the metamorphosis of these small communities into dense urban centres. This transformation has not been without its difficulties: rapid urbanisation has led to overcrowding, poor housing and health challenges. The need to develop appropriate infrastructure to meet the growing needs of the population has become obvious. While the growth of these populations has stimulated the local economy, it has also raised questions about quality of life and social disparities. The evolution of Saint-Étienne and Roubaix is representative of the impact of industrialisation on the transformation of small rural communities into large modern urban centres, with their share of benefits and challenges. | |||
Industrialisation led to the rapid and disorganised growth of industrial towns and cities, resulting in a marked contrast with the large cities that were modernising at the same time. Towns such as Seraing in Belgium, which rapidly industrialised thanks to its steelworks and mines, saw a considerable increase in their population without the urban planning necessary to accompany such expansion. These industrial towns, while having a population density equivalent to that of large cities, often lacked the corresponding infrastructure and services. Instead, their rapid growth had the characteristics of a sprawling village, with rudimentary organisation and inadequate public services, particularly in terms of public hygiene and education. The lack of infrastructure and public services was all the more problematic given the rapid growth in population. In these towns, the need for primary schools, health services and basic infrastructure far exceeded the capacity of local administrations to meet it. The finances of industrial towns were often precarious: they took on huge debts to build schools and other necessary infrastructure, as shown by the example of Seraing, which only repaid its last school building loan in 1961. The low tax base of these towns, due to the low wages of their workers, limited their ability to invest in the necessary improvements. So while the big cities were beginning to enjoy the attributes of modernity - running water, electricity, universities and efficient administrations - the industrial towns were struggling to provide basic services for their inhabitants. This situation reflects the social and economic inequalities inherent in the industrial era, where prosperity and technical progress coexisted with precarious and inadequate living conditions for a large proportion of the working population. | |||
== Housing conditions and hygiene == | |||
The industrial revolution revolutionised urban landscapes, and textile towns are a striking example of this. These areas, already densely populated before industrialisation, had to adapt quickly to a new wave of demographic influx. This was mainly due to the concentration of the textile industry in specific urban areas, which attracted workers from all over. To meet the resulting housing shortage, towns were forced to densify existing housing. Extra storeys were often added to buildings, exploiting every available square metre, even over narrow alleyways. This impromptu modification of the urban infrastructure created precarious living conditions, as these additional constructions were not always built with the necessary safety and comfort in mind. The infrastructure of these cities, such as sanitation, water supply and waste management systems, was often insufficient to cope with the rapid increase in population. Health and education services were struggling to keep up with growing demand. This rapid, sometimes anarchic, urbanisation led to difficult living conditions, with long-term consequences for the health and well-being of residents. These challenges reflect the tension between economic development and social needs in the rapidly changing cities of the Industrial Revolution. The authorities of the time were often overwhelmed by the scale of the changes and struggled to fund and implement the public services needed to keep pace with this explosive population growth. | |||
Dr. Kuborn was a doctor who worked in Seraing, Belgium, at the beginning of the 20th century. He witnessed at first hand the consequences of rapid industrialisation on the living conditions of workers and their families. Dr. Kuborn had a professional, and perhaps personal, interest in public health issues and urban hygiene. Doctors of the time were beginning to establish links between health and the environment, particularly the way in which substandard housing contributed to the spread of disease. They often played a key role in reforming living conditions by advocating improved urban planning, sanitation and housing standards. Dr. Kuborn shows that he was concerned about these issues and that he used his platform to draw attention to the unsanitary conditions in which the workers were forced to live. | |||
Dr. Kuborn depicts the deplorable state of workers' housing at the time. Referring to Seraing, he reports: "Dwellings were built as they were, most of them unsanitary, without a general plan in place. Low, sunken houses, without air or light; one room on the ground floor, no pavement, no cellar; an attic as an upper floor; ventilation through a hole, fitted with a pane of glass fixed into the roof; stagnation of household water; absence or inadequacy of latrines; overcrowding and promiscuity". He mentions poorly built houses, lacking fresh air, natural light and basic sanitary conditions such as adequate latrines. This image illustrates the lack of urban planning and disregard for the welfare of workers who, because of the need to house a growing working-class population near the factories, were forced to live in deplorable conditions. | |||
Dr. Kuborn | As Dr. Kuborn describes it: "It is in these insalubrious places, in these vile haunts, that epidemic diseases strike like a bird of prey swooping down on its victim. Cholera has shown us this, influenza reminds us of it, and perhaps typhus will give us a third example one of these days", he points out the disastrous consequences of these poor living conditions for the health of the inhabitants. Dr. Kuborn makes the link between unsanitary housing and the spread of epidemic diseases such as cholera, influenza and potentially typhus. The metaphor of the bird of prey swooping down on its victim is a powerful one, evoking the vulnerability of the workers who are like helpless prey in the face of the diseases proliferating in their unhealthy environment. | ||
These testimonies are representative of living conditions in European industrial towns in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. They reflect the grim reality of the Industrial Revolution, which, despite its technological and economic advances, often neglected the human and social aspects, leading to public health problems and marked social inequalities. These quotations call for reflection on the importance of urban planning, decent housing and access to adequate health services for all, issues that are still topical in many parts of the world. | |||
The development of the so-called "Black Country" regions, frequently associated with industrial areas where coal mining and steelmaking were predominant, was often rapid and disorganised. This anarchic growth was the result of accelerated urbanisation, where the need to house a large and growing workforce took precedence over urban planning and infrastructure. In many cases, living conditions in these areas were extremely precarious. Workers and their families were often housed in shanty towns or hastily constructed dwellings with little regard for durability, hygiene or comfort. These dwellings, often built without solid foundations, were not only unhealthy, but also dangerous, liable to collapse or become breeding grounds for disease. The density of the buildings, the lack of ventilation and light, and the absence of basic infrastructure such as running water and sanitation systems exacerbate public health problems. The cost of improving these areas was prohibitive, especially given their size and the poor quality of the existing buildings. As Dr. Kuborn pointed out in his comments on Seraing, setting up water and sewerage systems required major investments that local authorities were often unable to finance. Indeed, with a small tax base due to the low wages of the workers, these communities had few resources for investment in infrastructure. As a result, these communities found themselves caught in a vicious circle: inadequate infrastructure led to a deterioration in public health and quality of life, which in turn discouraged the investment and urban planning needed to improve the situation. In the end, the only viable solution often seemed to be to demolish existing structures and rebuild, a costly and disruptive process that was not always possible or achieved. | |||
Louis Pasteur's discoveries in the mid-nineteenth century about microbes and the importance of hygiene were fundamental to public health. However, the application of these hygiene principles in industrialised urban areas was complicated by a number of factors. Firstly, anarchic urbanisation, with development carried out without proper planning, has led to the creation of unsanitary housing and a lack of essential infrastructure. Installing water and sewerage systems in already densely built-up towns was extremely difficult and costly. Unlike planned neighbourhoods, where an efficient network of pipes could serve many inhabitants in a small area, sprawling shantytowns required kilometres of piping to connect each scattered dwelling. Secondly, land subsidence due to abandoned underground mining posed considerable risks to the integrity of the new infrastructure. The pipes could easily be damaged or destroyed by these ground movements, wiping out the efforts and investment made to improve hygiene. Thirdly, air pollution exacerbated the health problems even further. Smoke from factories and furnaces literally covered the towns with a layer of soot and pollutants, which not only made the air unhealthy to breathe but also contributed to the deterioration of buildings and infrastructure. All these factors confirm the difficulty of establishing hygiene and public health standards in already established industrial urban environments, especially when they have been developed hastily and without a long-term vision. This underlines the importance of urban planning and forecasting in the management of cities, particularly in the context of rapid industrial development. | |||
Germany, as a latecomer to the industrial revolution, has had the advantage of observing and learning from the mistakes and challenges faced by its neighbours such as Belgium and France. This enabled it to adopt a more methodical and planned approach to industrialisation, particularly with regard to workers' housing and town planning. The German authorities implemented policies that encouraged the construction of better quality housing for workers, as well as wider and better organised streets. This contrasted with the often chaotic and unhealthy conditions in industrial cities elsewhere, where rapid and unregulated growth had led to overcrowded and poorly equipped neighbourhoods. A key aspect of the German approach was a commitment to more progressive social policies, which recognised the importance of worker welfare to overall economic productivity. German industrial companies often took the initiative to build housing for their employees, with facilities such as gardens, baths and laundries, which contributed to workers' health and comfort. In addition, social legislation in Germany, such as the laws on health insurance, accident insurance and pension insurance introduced under Chancellor Otto von Bismarck in the 1880s, helped to establish a safety net for workers and their families. These efforts to improve workers' housing and living conditions, combined with preventive social legislation, helped Germany avoid some of the worst effects of rapid industrialisation. It also laid the foundations for a more stable society and for Germany's role as a major industrial power in later years. | |||
== Poor nutrition and low wages == | |||
== | |||
[[Fichier:Une alimentation déficiente et des salaires bas.png|300px|vignette]] | [[Fichier:Une alimentation déficiente et des salaires bas.png|300px|vignette]] | ||
Version du 1 décembre 2023 à 14:17
Based on a lecture by Michel Oris[1][2]
Agrarian Structures and Rural Society: Analysis of the Preindustrial European Peasantry ● The demographic regime of the Ancien Régime: homeostasis ● Evolution of Socioeconomic Structures in the Eighteenth Century: From the Ancien Régime to Modernity ● Origins and causes of the English industrial revolution ● Structural mechanisms of the industrial revolution ● The spread of the Industrial Revolution in continental Europe ● The Industrial Revolution beyond Europe: the United States and Japan ● The social costs of the Industrial Revolution ● Historical Analysis of the Cyclical Phases of the First Globalisation ● Dynamics of National Markets and the Globalisation of Product Trade ● The Formation of Global Migration Systems ● Dynamics and Impacts of the Globalisation of Money Markets : The Central Role of Great Britain and France ● The Transformation of Social Structures and Relations during the Industrial Revolution ● The Origins of the Third World and the Impact of Colonisation ● Failures and Obstacles in the Third World ● Changing Methods of Work: Evolving Production Relationships from the End of the Nineteenth to the Middle of the Twentieth Century ● The Golden Age of the Western Economy: The Thirty Glorious Years (1945-1973) ● The Changing World Economy: 1973-2007 ● The Challenges of the Welfare State ● Around colonisation: fears and hopes for development ● Time of Ruptures: Challenges and Opportunities in the International Economy ● Globalisation and modes of development in the "third world"
During the 19th century, Europe witnessed a profound metamorphosis - the Industrial Revolution - marked by unprecedented economic growth and a drive towards modernity. However, this period of growth and innovation was also synonymous with tumultuous social transformations and considerable humanitarian challenges. Delve into the English towns of the 1820s, walk through the steaming workshops of Le Creusot in the 1840s, or peer into the darkened alleys of East Belgium in the 1850s, and you'll see a striking contrast: technological progress and prosperity rubbed shoulders with exacerbated precariousness and chaotic urbanisation.
Rampant urbanisation, insalubrious housing, endemic diseases and deplorable working conditions defined the daily lives of many workers, with life expectancy dropping dramatically to 30 years in industrial centres. Hardy and bold people left the countryside to throw themselves into the arms of voracious industry, contributing to a relative improvement in mortality in rural areas, but at the cost of an overwhelming urban existence. The deadly influence of the environment was even more pernicious than the rigours of factory work.
In the midst of this era of glaring inequality, epidemics such as cholera highlighted the failings of modern society and the vulnerability of underprivileged populations. The social and political reaction to this health crisis, from the repression of workers' movements to the bourgeois fear of insurrection, revealed a growing divide between the classes. This division was no longer dictated by blood, but by social status, reinforcing a hierarchy that further marginalised the workers.
Against this backdrop, the writings of social thinkers like Eugène Buret become poignant testaments to the industrial age, expressing both criticism of an alienating modernity and hope for a reform that would integrate all citizens into the fabric of a fairer political and social community. These historical reflections offer us a perspective on the complexity of social change and the enduring challenges of equity and human solidarity.
The new spaces
Industrial basins and towns
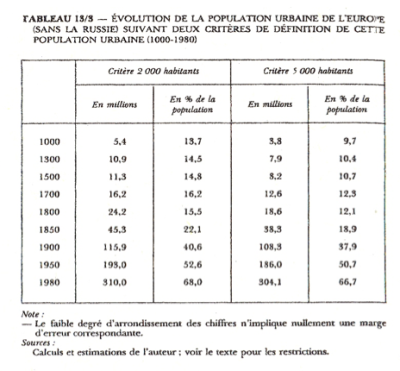
This table gives an historical overview of the growth of the urban population in Europe, excluding Russia, through the ages, highlighting two population thresholds for defining a city: those with more than 2,000 inhabitants and those with more than 5,000 inhabitants. At the start of the second millennium, around the year 1000, Europe already had a significant proportion of its population living in urban areas. Towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants were home to 5.4 million people, making up 13.7% of the total population. If we raise the threshold to 5,000 inhabitants, we find 5.8 million people, representing 9.7% of the population. As we move towards 1500, we see a slight proportional increase in the urban population. In towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants, it rose to 10.9 million, or 14.5% of the population. In towns with more than 5,000 residents, the number rose to 7.9 million, equivalent to 10.4% of the total population. The impact of the Industrial Revolution became clearly visible in 1800, with a significant jump in the number of city dwellers. There were 26.2 million people living in towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants, who now accounted for 16.2% of the total population. For towns with more than 5,000 inhabitants, the number rises to 18.6 million, representing 12.5% of the population. Urbanisation accelerated further in the mid-nineteenth century, and by 1850 there were 45.3 million people living in towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants, corresponding to 22.1% of the total population. Towns with more than 5,000 inhabitants were home to 38.3 million people, or 18.9% of the population. The twentieth century marked a turning point with massive urbanisation. By 1950, the population of towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants had risen to 193.0 million, representing a majority of 53.6% of the total population. Cities with more than 5,000 inhabitants were not to be outdone, with a population of 186.0 million, or 50.7% of all Europeans. Finally, in 1980, the urban phenomenon reached new heights, with 310.0 million Europeans living in towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants, representing 68.0% of the population. The figure for towns with more than 5,000 inhabitants was 301.1 million, equivalent to 66.7% of the population. The table thus reveals a spectacular transition from a predominantly rural to a predominantly urban Europe, a process that accelerated with industrialisation and continued throughout the 20th century.
According to the economic historian Paul Bairoch, the society of the Ancien Régime was characterised by a natural limit of the urban population to around 15% of the total population. This idea stems from the observation that, until 1800, the vast majority of the population - between 70% and 75%, and even 80% during the winter months when agricultural activity slowed down - had to work in agriculture to produce enough food. Food production thus limited the size of urban populations, as agricultural surpluses had to feed city dwellers, who were often regarded as "parasites" because they did not contribute directly to agricultural production. The population not involved in agriculture, around 25-30%, was spread across other sectors of activity. But not all were urban dwellers; some lived and worked in rural areas, such as parish priests and other professionals. This meant that the proportion of the population that could live in the city without overburdening the productive capacity of agriculture was a maximum of 15%. This figure was not due to any formal legislation but represented an economic and social constraint dictated by the level of agricultural and technological development at the time. With the advent of the industrial revolution and advances in agriculture, the capacity of societies to feed larger urban populations increased, allowing this hypothetical limit to be exceeded and paving the way for increasing urbanisation.
The demographic and social landscape of Europe has undergone considerable change since the mid-19th century. Around 1850, the beginnings of industrialisation began to alter the balance between rural and urban populations. Technological advances in agriculture began to reduce the amount of labour needed to produce food, and expanding factories in the cities began to attract workers from the countryside. However, even with these changes, peasants and rural life remained predominant at the end of the 19th century. The majority of Europe's population still lived in farming communities, and it was only gradually that towns grew and societies became more urbanised. It was not until the mid-twentieth century, particularly in the 1950s, that we saw a major change, with the rate of urbanisation in Europe crossing the 50% threshold. This marked a turning point, indicating that for the first time in history, a majority of the population was living in cities rather than in rural areas. Today, with an urbanisation rate in excess of 70%, cities have become the dominant living environment in Europe. England, with cities such as Manchester and Birmingham, was the starting point for this change, followed by other industrial regions such as the Ruhr in Germany and Northern France, both of which were rich in resources and industries that attracted large workforces. These regions were the nerve centres of industrial activity and served as models for urban expansion across the continent.
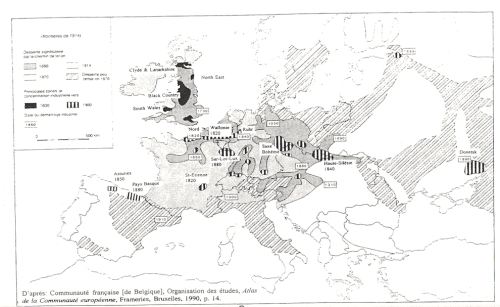
This map is a graphic representation of Europe in the pre-industrial era, highlighting the areas that were major industrial centres before the First World War. It highlights the intensity and specialisation of industrial activities through different symbols and patterns that identify the predominant types of industry in each region. Dark areas marked by symbols of blast furnaces and coal mines indicate industrial basins focused on metallurgy and mining. Places like the Ruhr, Northern France, Silesia, the Black Country region of Belgium and South Wales stand out as key industrial centres, showing the importance of coal and steel in the European economy at the time. Areas with stripes indicate regions where the textile industry and mechanical engineering were strongly represented. This geographical distribution shows that industrialisation was not uniform but rather concentrated in certain places, depending on available resources and capital investment. Distinct features denote regions specialising in iron and steel, notably Lorraine and parts of Italy and Spain, suggesting that the steel industry was also widespread, though less dominant than the coal industry. Maritime symbols, such as ships, are positioned in areas such as the North East of England, suggesting the importance of shipbuilding, which was consistent with the expansion of European colonial empires and international trade. This map provides a striking illustration of how the Industrial Revolution changed the economic and social landscape of Europe. The industrial regions identified were probably hotspots for internal migration, attracting workers from the countryside to the growing cities. This had a profound effect on demographic structure, leading to rapid urbanisation, the development of the working classes and the emergence of new social challenges such as pollution and substandard housing. The map highlights the unevenness of industrial development across the continent, reflecting the regional disparities that have emerged in terms of economic opportunities, living conditions and population growth. These industrial regions exerted a decisive influence on the economic and social trajectories of their respective countries, an influence that lasted well beyond the classical industrial era.
The historical map of pre-industrial Europe depicts two main types of industrial region that were crucial to the continent's economic and social transformation: the 'black countries' and the textile towns. The "black countries" are represented by areas darkened with icons of blast furnaces and mines. These regions were the heart of heavy industry, centred mainly on coal mining and steel production. Coal was the basis of the industrial economy, powering the machines and factories that underpinned the Industrial Revolution. Regions such as the Ruhr in Germany, Northern France, Silesia and the Black Country in Belgium were notable industrial centres, characterised by a dense concentration of coal- and steel-related activities. In contrast, the textile towns, indicated by striped areas, specialised in the production of textiles, a sector that was also vital during the Industrial Revolution. These towns took advantage of mechanisation to mass-produce fabrics, which elevated them to the status of major industrial centres. The textile revolution began in England and quickly spread to other parts of Europe, giving rise to numerous industrial towns centred on spinning and weaving. The distinction between these two types of industrial region is crucial. Whereas the black countries were often characterised by pollution, difficult working conditions and a significant environmental impact, textile towns, while also having their own social and health challenges, were generally less polluting and could be more dispersed in character, as textile mills required less concentration of heavy resources than blast furnaces and mines. The map therefore highlights not only the geographical distribution of industrialisation, but also the diversity of industries that made up the economic fabric of Europe at that time. Each of these regions had distinct social effects, influencing the lives of workers, the structure of social classes, urbanisation and the evolution of urban and rural societies in the context of the Industrial Revolution.
Black Country" is an evocative term used to describe the regions that became the scene of coal mining and metal production during the Industrial Revolution. The term refers to the omnipresent smoke and soot in these areas, the result of the intense activity of blast furnaces and foundries that transformed peaceful villages into industrial towns in a very short space of time. The atmosphere was so polluted that the sky and buildings were literally blackened, hence the name "black countries". This phenomenon of rapid industrialisation turned the static world of the time on its head, marking the start of an era in which economic growth became the norm and stagnation synonymous with crisis. Coalmining in particular catalysed this transformation by requiring a huge workforce. The coal mines and iron and steel industries became the driving force behind a dazzling demographic expansion, as in the case of Seraing, where the arrival of the industrialist Cockerill saw the population rise from 2,000 to 44,000 in the space of a century. Workers, often recruited from the rural population, were employed en masse in the coal mines, which required considerable physical strength, particularly for pick-axe work before automation in the 1920s. This demand for labour contributed to a rural exodus towards these centres of industrial activity. Ironworks required large open spaces because of the weight and size of the materials handled, so they could not be established in already dense towns. Industrialisation therefore moved to the countryside, where space was available and coal was within reach. This led to the creation of vast industrial basins, radically changing the landscape as well as the social and economic structure of the regions concerned. These industrial transformations also brought profound changes to society. Daily life was radically altered, with the birth of the working class and the deterioration of living conditions due to pollution and rapid urbanisation. The "black countries" became symbols of progress, but also witnesses to the social and environmental costs of the industrial revolution.
Victor Hugo described these landscapes: "When you pass the place called Petite-Flémalle, the sight becomes inexpressible and truly magnificent. The whole valley seems to be pitted with erupting craters. Some of them spew out swirls of scarlet steam spangled with sparks behind the undergrowth; others gloomily outline the black silhouette of villages against a red background; elsewhere flames appear through the cracks in a group of buildings. You would think that an enemy army had just crossed the country, and that twenty villages had been sacked, offering you at the same time in this dark night all the aspects and all the phases of the fire, some engulfed in flames, some smoking, others blazing. This spectacle of war is given by peace; this appalling copy of devastation is made by industry. You are simply looking at Mr Cockerill's blast furnaces.
This quotation from Victor Hugo, taken from his "Journey along the Rhine" written in 1834, is a powerful testimony to the visual and emotional impact of industrialisation in Europe. Hugo, known for his literary work but also for his interest in the social issues of his time, describes here with dark and powerful lyricism the Meuse valley in Belgium, near Petite-Flémalle, marked by John Cockerill's industrial installations. Hugo uses images of destruction and war to describe the industrial scene before him. The blast furnaces light up the night, resembling erupting craters, burning villages, or even a land ravaged by an enemy army. There is a striking contrast between peace and war; the scene he describes is not the result of armed conflict but of peaceful, or at least non-military, industrialisation. The "erupting craters" evoke the intensity and violence of industrial activity, which marks the landscape as indelibly as war itself. This dramatic description underlines both the fascination and the repulsion that industrialisation can arouse. On the one hand, there is the magnificence and power of human transformation; on the other, the destruction of a way of life and an environment. The references to fires and the black silhouettes of villages project the image of a land in the grip of almost apocalyptic forces, reflecting the ambivalence of industrial progress. To put this quotation into context, we need to remember that Europe in the 1830s was in the midst of an industrial revolution. Technological innovations, the intensive use of coal and the development of metallurgy were radically transforming the economy, society and the environment. Cockerill was a leading industrial entrepreneur of this era, having developed one of the largest industrial complexes in Europe in Seraing, Belgium. The rise of this industry was synonymous with economic prosperity, but also with social upheaval and considerable environmental impact, including pollution and landscape degradation. With this quote, Victor Hugo invites us to reflect on the dual face of industrialisation, which is both a source of progress and devastation. In so doing, he reveals the ambiguity of an era when human genius, capable of transforming the world, must also reckon with the sometimes dark consequences of these transformations.
The textile towns of the Industrial Revolution represent a crucial aspect of the economic and social transformation that began in the 18th century. In these urban centres, the textile industry played a driving role, facilitated by the extreme division of labour into distinct processes such as weaving, spinning and dyeing. Unlike the heavy coal and steel industries, which were often located in rural or peri-urban areas for logistical and space reasons, textile factories were able to take advantage of the verticality of existing or purpose-built urban buildings to maximise limited floor space. These factories became a natural part of the urban landscape, helping to redefine the towns and cities of northern France, Belgium and other regions, which saw their population density increase dramatically. The transition from craft and proto-industry to large-scale industrial production led to the bankruptcy of many craftsmen, who then turned to factory work. Textile industrialisation transformed towns into veritable industrial metropolises, leading to rapid and often disorganised urbanisation, marked by unbridled construction in every available space. The massive increase in textile production was not accompanied by an equivalent increase in the number of workers, thanks to the productivity gains achieved through industrialisation. The textile towns of the time were therefore characterised by an extreme concentration of the workforce in the factories, which became the centre of social and economic life, eclipsing traditional institutions such as the town hall or public squares. Public space was dominated by the factory, which defined not only the urban landscape, but also the rhythm and structure of community life. This transformation also influenced the social composition of towns, attracting merchants and entrepreneurs who had benefited from the economic growth of the 19th century. These new elites often supported and invested in the development of industrial and residential infrastructures, thereby contributing to urban expansion. In short, textile towns embody a fundamental chapter in industrial history, illustrating the close link between technological progress, social change and the reconfiguration of the urban environment.
Two types of demographic development
The Industrial Revolution led to major migration from rural to urban areas, irreversibly transforming European societies. In the context of textile towns, this rural exodus was particularly pronounced. Craftsmen and proto-industrial workers, traditionally dispersed in the countryside where they worked at home or in small workshops, were forced to congregate in the industrial cities. This was due to the need to be close to the factories, as long journeys between home and work became impractical with the increasingly regulated work structure of the factory. The concentration of workers in cities had several consequences. On the one hand, the proximity of workers to production sites enabled more efficient management and rationalisation of the work process, leading to an explosion in productivity without necessarily increasing the number of workers employed. Indeed, innovations in production techniques, such as the use of steam engines and the automation of weaving and spinning processes, have considerably increased yields while maintaining or reducing the workforce required. In cities, the concentration of the population also led to rapid densification and urbanisation, as shown by the example of Verviers. The population of this Belgian textile town almost tripled over the course of the nineteenth century, rising from 35,000 at the start to 100,000 by the end of the century. This rapid expansion of the urban population often led to hasty urbanisation and difficult living conditions, as the existing infrastructure was rarely adequate to cope with such an influx. The concentration of the workforce also changed the social structure of cities, creating new classes of industrial workers and altering existing socio-economic dynamics. It also had an impact on the urban fabric, with the construction of housing for workers, the expansion of urban services and facilities, and the development of new forms of community life centred around the factory rather than the traditional structures of the city. Ultimately, the phenomenon of textile towns during the Industrial Revolution illustrates the transformative power of industrialisation on settlement patterns, the economy and society as a whole.
The steel regions, often referred to as 'black countries' because of the soot and pollution from factories and mines, illustrate another facet of the impact of industrialisation on demography and urban development. The black countries were centred on the coal and iron industries, which were essential catalysts for the industrial revolution. The demographic explosion in these regions was due less to an increase in the number of workers per mine or factory than to the emergence of new labour-intensive industries. Although mechanisation was progressing, it was not yet replacing the need for workers in coal mines and ironworks. For example, although the steam engine made it possible to ventilate the galleries and increase the productivity of the mines, extracting coal was still a very laborious job requiring large numbers of workers. The demographic growth in towns such as Liège, where the population rose from 50,000 to 400,000, bears witness to this industrial expansion. The coalfields and steelworks became centres of attraction for workers looking for work, leading to rapid growth in the surrounding towns. These workers were often migrants from the countryside or other less industrialised regions, attracted by the job opportunities created by these new industries. These industrial towns grew at an impressive rate, often without the planning or infrastructure needed to adequately accommodate their new population. The result was precarious living conditions, with overcrowded and unhealthy housing, public health problems and growing social tensions. These challenges would eventually lead to urban and social reforms in the following centuries, but during the Industrial Revolution, these regions were marked by rapid and often chaotic transformation.
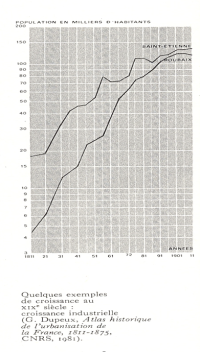
This graph shows the significant demographic growth of Saint-Étienne and Roubaix, two emblematic cities of the French industrial epic, over the period from 1811 to 1911. Over the course of the century, these towns saw their populations grow considerably as a result of rampant industrialisation. In Roubaix, the growth was particularly striking. Known for its flourishing textile industry, the town grew from fewer than 10,000 inhabitants at the start of the century to around 150,000 at its end. The labour-intensive textile industry led to a massive migration of rural populations to Roubaix, radically transforming its social and urban landscape. Saint-Étienne followed a similar upward curve, although its numbers remained lower than those of Roubaix. As a strategic centre for metallurgy and arms manufacture, the town also created a huge demand for skilled and unskilled workers, which contributed to its demographic boom. Industrialisation was the catalyst for a major social change, reflected in the metamorphosis of these small communities into dense urban centres. This transformation has not been without its difficulties: rapid urbanisation has led to overcrowding, poor housing and health challenges. The need to develop appropriate infrastructure to meet the growing needs of the population has become obvious. While the growth of these populations has stimulated the local economy, it has also raised questions about quality of life and social disparities. The evolution of Saint-Étienne and Roubaix is representative of the impact of industrialisation on the transformation of small rural communities into large modern urban centres, with their share of benefits and challenges.
Industrialisation led to the rapid and disorganised growth of industrial towns and cities, resulting in a marked contrast with the large cities that were modernising at the same time. Towns such as Seraing in Belgium, which rapidly industrialised thanks to its steelworks and mines, saw a considerable increase in their population without the urban planning necessary to accompany such expansion. These industrial towns, while having a population density equivalent to that of large cities, often lacked the corresponding infrastructure and services. Instead, their rapid growth had the characteristics of a sprawling village, with rudimentary organisation and inadequate public services, particularly in terms of public hygiene and education. The lack of infrastructure and public services was all the more problematic given the rapid growth in population. In these towns, the need for primary schools, health services and basic infrastructure far exceeded the capacity of local administrations to meet it. The finances of industrial towns were often precarious: they took on huge debts to build schools and other necessary infrastructure, as shown by the example of Seraing, which only repaid its last school building loan in 1961. The low tax base of these towns, due to the low wages of their workers, limited their ability to invest in the necessary improvements. So while the big cities were beginning to enjoy the attributes of modernity - running water, electricity, universities and efficient administrations - the industrial towns were struggling to provide basic services for their inhabitants. This situation reflects the social and economic inequalities inherent in the industrial era, where prosperity and technical progress coexisted with precarious and inadequate living conditions for a large proportion of the working population.
Housing conditions and hygiene
The industrial revolution revolutionised urban landscapes, and textile towns are a striking example of this. These areas, already densely populated before industrialisation, had to adapt quickly to a new wave of demographic influx. This was mainly due to the concentration of the textile industry in specific urban areas, which attracted workers from all over. To meet the resulting housing shortage, towns were forced to densify existing housing. Extra storeys were often added to buildings, exploiting every available square metre, even over narrow alleyways. This impromptu modification of the urban infrastructure created precarious living conditions, as these additional constructions were not always built with the necessary safety and comfort in mind. The infrastructure of these cities, such as sanitation, water supply and waste management systems, was often insufficient to cope with the rapid increase in population. Health and education services were struggling to keep up with growing demand. This rapid, sometimes anarchic, urbanisation led to difficult living conditions, with long-term consequences for the health and well-being of residents. These challenges reflect the tension between economic development and social needs in the rapidly changing cities of the Industrial Revolution. The authorities of the time were often overwhelmed by the scale of the changes and struggled to fund and implement the public services needed to keep pace with this explosive population growth.
Dr. Kuborn was a doctor who worked in Seraing, Belgium, at the beginning of the 20th century. He witnessed at first hand the consequences of rapid industrialisation on the living conditions of workers and their families. Dr. Kuborn had a professional, and perhaps personal, interest in public health issues and urban hygiene. Doctors of the time were beginning to establish links between health and the environment, particularly the way in which substandard housing contributed to the spread of disease. They often played a key role in reforming living conditions by advocating improved urban planning, sanitation and housing standards. Dr. Kuborn shows that he was concerned about these issues and that he used his platform to draw attention to the unsanitary conditions in which the workers were forced to live.
Dr. Kuborn depicts the deplorable state of workers' housing at the time. Referring to Seraing, he reports: "Dwellings were built as they were, most of them unsanitary, without a general plan in place. Low, sunken houses, without air or light; one room on the ground floor, no pavement, no cellar; an attic as an upper floor; ventilation through a hole, fitted with a pane of glass fixed into the roof; stagnation of household water; absence or inadequacy of latrines; overcrowding and promiscuity". He mentions poorly built houses, lacking fresh air, natural light and basic sanitary conditions such as adequate latrines. This image illustrates the lack of urban planning and disregard for the welfare of workers who, because of the need to house a growing working-class population near the factories, were forced to live in deplorable conditions.
As Dr. Kuborn describes it: "It is in these insalubrious places, in these vile haunts, that epidemic diseases strike like a bird of prey swooping down on its victim. Cholera has shown us this, influenza reminds us of it, and perhaps typhus will give us a third example one of these days", he points out the disastrous consequences of these poor living conditions for the health of the inhabitants. Dr. Kuborn makes the link between unsanitary housing and the spread of epidemic diseases such as cholera, influenza and potentially typhus. The metaphor of the bird of prey swooping down on its victim is a powerful one, evoking the vulnerability of the workers who are like helpless prey in the face of the diseases proliferating in their unhealthy environment.
These testimonies are representative of living conditions in European industrial towns in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. They reflect the grim reality of the Industrial Revolution, which, despite its technological and economic advances, often neglected the human and social aspects, leading to public health problems and marked social inequalities. These quotations call for reflection on the importance of urban planning, decent housing and access to adequate health services for all, issues that are still topical in many parts of the world.
The development of the so-called "Black Country" regions, frequently associated with industrial areas where coal mining and steelmaking were predominant, was often rapid and disorganised. This anarchic growth was the result of accelerated urbanisation, where the need to house a large and growing workforce took precedence over urban planning and infrastructure. In many cases, living conditions in these areas were extremely precarious. Workers and their families were often housed in shanty towns or hastily constructed dwellings with little regard for durability, hygiene or comfort. These dwellings, often built without solid foundations, were not only unhealthy, but also dangerous, liable to collapse or become breeding grounds for disease. The density of the buildings, the lack of ventilation and light, and the absence of basic infrastructure such as running water and sanitation systems exacerbate public health problems. The cost of improving these areas was prohibitive, especially given their size and the poor quality of the existing buildings. As Dr. Kuborn pointed out in his comments on Seraing, setting up water and sewerage systems required major investments that local authorities were often unable to finance. Indeed, with a small tax base due to the low wages of the workers, these communities had few resources for investment in infrastructure. As a result, these communities found themselves caught in a vicious circle: inadequate infrastructure led to a deterioration in public health and quality of life, which in turn discouraged the investment and urban planning needed to improve the situation. In the end, the only viable solution often seemed to be to demolish existing structures and rebuild, a costly and disruptive process that was not always possible or achieved.
Louis Pasteur's discoveries in the mid-nineteenth century about microbes and the importance of hygiene were fundamental to public health. However, the application of these hygiene principles in industrialised urban areas was complicated by a number of factors. Firstly, anarchic urbanisation, with development carried out without proper planning, has led to the creation of unsanitary housing and a lack of essential infrastructure. Installing water and sewerage systems in already densely built-up towns was extremely difficult and costly. Unlike planned neighbourhoods, where an efficient network of pipes could serve many inhabitants in a small area, sprawling shantytowns required kilometres of piping to connect each scattered dwelling. Secondly, land subsidence due to abandoned underground mining posed considerable risks to the integrity of the new infrastructure. The pipes could easily be damaged or destroyed by these ground movements, wiping out the efforts and investment made to improve hygiene. Thirdly, air pollution exacerbated the health problems even further. Smoke from factories and furnaces literally covered the towns with a layer of soot and pollutants, which not only made the air unhealthy to breathe but also contributed to the deterioration of buildings and infrastructure. All these factors confirm the difficulty of establishing hygiene and public health standards in already established industrial urban environments, especially when they have been developed hastily and without a long-term vision. This underlines the importance of urban planning and forecasting in the management of cities, particularly in the context of rapid industrial development.
Germany, as a latecomer to the industrial revolution, has had the advantage of observing and learning from the mistakes and challenges faced by its neighbours such as Belgium and France. This enabled it to adopt a more methodical and planned approach to industrialisation, particularly with regard to workers' housing and town planning. The German authorities implemented policies that encouraged the construction of better quality housing for workers, as well as wider and better organised streets. This contrasted with the often chaotic and unhealthy conditions in industrial cities elsewhere, where rapid and unregulated growth had led to overcrowded and poorly equipped neighbourhoods. A key aspect of the German approach was a commitment to more progressive social policies, which recognised the importance of worker welfare to overall economic productivity. German industrial companies often took the initiative to build housing for their employees, with facilities such as gardens, baths and laundries, which contributed to workers' health and comfort. In addition, social legislation in Germany, such as the laws on health insurance, accident insurance and pension insurance introduced under Chancellor Otto von Bismarck in the 1880s, helped to establish a safety net for workers and their families. These efforts to improve workers' housing and living conditions, combined with preventive social legislation, helped Germany avoid some of the worst effects of rapid industrialisation. It also laid the foundations for a more stable society and for Germany's role as a major industrial power in later years.
Poor nutrition and low wages
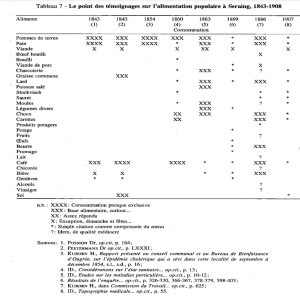
Le tableau présenté offre une fenêtre historique sur les habitudes alimentaires à Seraing, en Belgique, de 1843 à 1908. Chaque colonne correspond à une année ou période spécifique, et la consommation des différents aliments est codifiée de manière à indiquer leur prévalence dans l'alimentation locale. Les codes varient de "XXXX" pour une consommation quasi exclusive, jusqu'à "X" pour une consommation moindre. Un astérisque "*" signale une simple mention de l'aliment, tandis que les annotations telles que "Accessoire" ou "Exception, fête..." suggèrent une consommation occasionnelle ou liée à des événements particuliers. Des points d'interrogation "?" sont utilisés lorsque la consommation est incertaine ou non documentée, et la mention "de qualité médiocre" laisse supposer une moindre qualité des produits à certains moments. L'analyse de ce tableau révèle plusieurs aspects notables de l'alimentation de l'époque. Les pommes de terre et le pain apparaissent comme des éléments fondamentaux, reflétant leur rôle central dans l'alimentation des classes laborieuses en Europe durant cette période. La viande, avec une présence notable de bœuf bouilli et de charcuterie, est consommée de façon moins régulière, ce qui peut indiquer des variations de revenu ou des préférences alimentaires saisonnières. Le café et la chicorée semblent gagner en popularité, ce qui pourrait correspondre à une augmentation de la consommation de stimulants pour faire face à de longues heures de travail. La mention de graisses comme le lard et la graisse commune témoigne d'une alimentation riche en calories, essentielle pour soutenir le travail physique exigeant de l'époque. La consommation d'alcool est incertaine vers la fin de la période étudiée, suggérant des changements dans les habitudes de consommation ou peut-être dans la disponibilité des boissons alcoolisées. Les fruits, le beurre et le lait montrent une variabilité qui pourrait refléter les fluctuations de l'approvisionnement ou des préférences alimentaires au fil du temps. L'évolution des habitudes alimentaires indiquée par ce tableau peut être liée aux transformations socio-économiques majeures de la période, telles que l'industrialisation et l'amélioration des infrastructures de transport et de distribution. Cela suggère également une possible amélioration du niveau de vie et des conditions sociales au sein de la communauté de Seraing, bien que cela nécessiterait une analyse plus approfondie pour être confirmé. Dans l'ensemble, ce tableau est un document précieux pour comprendre la culture alimentaire dans une ville industrielle et peut donner des indications sur l'état de santé et la qualité de vie de ses résidents à l'aube de la révolution industrielle.
L'émergence des marchés dans les villes industrielles au XIXe siècle fut un processus lent et souvent chaotique. Dans ces villes nouvellement formées ou en rapide expansion à cause de l'industrialisation, la structure commerciale peinait à suivre le rythme de la croissance démographique et de l'afflux des travailleurs. Les épiciers et les commerçants étaient rares et, en raison de leur rareté et de l'absence de concurrence, ils pouvaient se permettre de fixer des prix élevés pour les denrées alimentaires et les biens de consommation courants. Cette situation avait un impact direct sur les ouvriers, dont la majorité vivait déjà dans des conditions précaires, avec des salaires souvent insuffisants pour couvrir leurs besoins de base. L'exploitation des ouvriers par les commerçants se manifestait par des pratiques de prix abusifs qui entraînaient l'endettement des travailleurs. Cette précarité économique était exacerbée par la faiblesse des salaires et la vulnérabilité face aux aléas économiques et sanitaires. Dans ce contexte, les entreprises cherchaient des solutions pour pallier le manque de services et de commerces, et pour assurer un certain contrôle sur leur main-d'œuvre. Une de ces solutions fut le système du truck (truck-system), un système de paiement en nature où une partie du salaire des ouvriers était versée sous forme de denrées alimentaires ou de biens de consommation domestiques. L'entreprise achetait ces produits en gros et les redistribuait à ses employés, souvent à des prix déterminés par elle-même. Ce système avait l'avantage pour l'entreprise de fidéliser et de contrôler sa main-d'œuvre, tout en garantissant un débouché pour certains produits. Toutefois, le truck-system avait des inconvénients majeurs pour les travailleurs. Il limitait leur liberté de choix en matière de consommation et les rendait dépendants de l'entreprise pour leurs besoins essentiels. De plus, la qualité des biens fournis pouvait être médiocre, et les prix fixés par l'entreprise étaient souvent élevés, ce qui aggravait encore l'endettement des ouvriers. La mise en place de ce système souligne l'importance de l'entreprise dans la vie quotidienne des travailleurs de l'époque et illustre les difficultés de ces derniers à accéder à des biens de consommation de manière autonome. Cela reflète également la dimension sociale et économique du travail industriel, où l'entreprise n'est pas seulement un lieu de production mais aussi un acteur central dans la vie des ouvriers, influençant leur alimentation, leur logement et leur santé.
La perception de l'ouvrier comme immature au XIXe siècle est une facette de la mentalité paternaliste de l'époque, où les propriétaires d'usines et les élites sociales croyaient souvent que les travailleurs n'avaient ni la discipline ni la sagesse pour gérer leur propre bien-être, en particulier en ce qui concerne les finances. Cette vision était renforcée par des préjugés de classe et par l'observation des difficultés des ouvriers à s'élever au-dessus des conditions de pauvreté et de l'environnement souvent misérable dans lequel ils vivaient. En réponse à cette perception, ainsi qu'aux conditions de vie abjectes des travailleurs, un débat s'est engagé sur la nécessité d'un salaire minimum qui permettrait aux ouvriers de subvenir à leurs besoins sans tomber dans ce que les élites considéraient comme des comportements dépravés (la "débauche"). La débauche, dans ce contexte, pourrait inclure l'alcoolisme, le jeu, ou d'autres activités jugées improductives ou nuisibles à l'ordre social et à la moralité. L'idée derrière le salaire minimum était de fournir une sécurité financière de base qui pourrait, théoriquement, encourager les travailleurs à mener une vie plus stable et "morale". Il était supposé que si les travailleurs avaient suffisamment d'argent pour vivre, ils seraient moins enclins à dépenser leur argent de manière irresponsable. Cependant, cette approche ne prenait pas toujours en compte les réalités complexes de la vie ouvrière. Les bas salaires, les longues heures de travail et les conditions de vie difficiles pouvaient conduire à des comportements que les élites considéraient comme de la débauche, mais qui pouvaient être des moyens pour les ouvriers de faire face à la dureté de leur existence. Le mouvement pour un salaire minimum peut être vu comme une reconnaissance précoce des droits des travailleurs et un pas vers la réglementation du travail, bien qu'il fût aussi teinté de condescendance et de contrôle social. Ce débat a jeté les bases des discussions ultérieures sur les droits des travailleurs, la législation du travail, et la responsabilité sociale des entreprises qui ont continué à évoluer bien après le XIXe siècle.
La loi d'Engel, du nom de l'économiste allemand Ernst Engel, est une observation empirique qui souligne une relation inverse entre le revenu d'un ménage et la proportion de celui-ci dépensée pour la nourriture. Selon cette loi, plus un ménage est pauvre, plus il doit consacrer une grande part de ses ressources limitées à des besoins essentiels comme la nourriture, parce que ces dépenses sont incompressibles et ne peuvent être réduites au-delà d'un certain point sans affecter la survie. Cette loi est devenue un indicateur important pour mesurer la pauvreté et le niveau de vie. Si un ménage consacre une grande partie de son budget à l'alimentation, cela indique souvent un niveau de vie bas, car il reste peu pour d'autres aspects de la vie tels que le logement, la santé, l'éducation et les loisirs. Au XIXe siècle, dans le contexte de la révolution industrielle, beaucoup d'ouvriers vivaient dans des conditions de pauvreté et leurs salaires étaient si bas qu'ils ne pouvaient pas payer d'impôts. Cela reflétait non seulement l'étendue de la pauvreté, mais également le manque de moyens financiers des gouvernements pour améliorer les infrastructures et les services publics, car une base fiscale plus large est souvent nécessaire pour financer de tels développements. Avec le temps, à mesure que la révolution industrielle progressait et que les économies se développaient, les salaires réels commencèrent lentement à augmenter. Cela fut en partie dû à l'augmentation de la productivité grâce à de nouvelles technologies et à la mécanisation, mais aussi en raison des luttes et des revendications des ouvriers pour de meilleures conditions de travail et des salaires plus élevés. Ces changements ont contribué à une meilleure répartition de la richesse et à une réduction de la part des dépenses consacrées à l'alimentation, reflétant une amélioration du niveau de vie général.
La loi ne stipule pas que les dépenses alimentaires diminuent en valeur absolue avec l'augmentation du revenu, mais plutôt que leur part relative dans le budget total diminue. Ainsi, une personne ou un ménage plus aisé peut absolument dépenser plus en termes absolus sur la nourriture que quelqu'un de moins aisé, tout en consacrant une plus petite proportion de son budget total à cette catégorie de dépenses. Par exemple, une famille à faible revenu pourrait dépenser 50% de son revenu total en nourriture, alors qu'une famille aisée pourrait n'en dépenser que 15%. Cependant, en termes de montant réel, la famille aisée peut dépenser plus sur la nourriture que la famille à faible revenu simplement parce que son revenu total est plus élevé. Cette observation est importante car elle permet d'analyser et de comprendre les habitudes de consommation en fonction des revenus, ce qui peut être crucial pour la formulation de politiques économiques et sociales, en particulier celles liées à la fiscalité, aux subventions alimentaires, et aux programmes d'aide sociale. Cela fournit également des informations précieuses sur la structure socio-économique de la population et sur les changements dans les modes de vie au fur et à mesure que le niveau de vie s'améliore.
Le jugement ultime : la mortalité des populations industrielles
Le paradoxe de la croissance
L'ère de la révolution industrielle et de l'expansion économique qui s'est déroulée au XIXe siècle a été une période de transformations profondes et contrastées. D'un côté, il y a eu une croissance économique significative et un progrès technique sans précédent. D'un autre côté, cela s'est souvent traduit par des conditions de vie extrêmement difficiles pour les ouvriers dans les centres urbains en expansion rapide. Il faut mettre en lumière une réalité sombre de cette période: l'urbanisation rapide et non réglementée (ce que certains appellent "urbanisation sauvage") a conduit à des conditions de vie insalubres. Les villes industrielles, qui se sont développées à un rythme effréné pour loger une main-d'œuvre toujours plus nombreuse, étaient souvent dépourvues d'infrastructures adéquates pour l'assainissement et l'accès à l'eau potable, ce qui a entraîné la propagation de maladies et une baisse de l'espérance de vie. Dans des villes comme les villes anglaises du début du XIXe siècle, Le Creusot en France dans les années 1840, la région de la Belgique orientale autour des années 1850-1860, ou Bilbao en Espagne au tournant du XXe siècle - l'industrialisation s'est accompagnée de conséquences humaines dévastatrices. Les travailleurs et leurs familles, souvent entassés dans des logements surpeuplés et précaires, étaient exposés à un environnement toxique, tant au travail qu'à la maison, avec une espérance de vie tombant à des niveaux aussi bas que 30 ans, reflétant les conditions de travail et de vie éprouvantes. Ce contraste entre les zones urbaines et rurales était également marqué. Alors que les villes industrielles souffraient, les campagnes pouvaient connaître des améliorations de la qualité de vie grâce à une meilleure répartition des ressources issues de la croissance économique et à un environnement moins concentré et moins pollué. Cette période de l'histoire illustre de manière poignante les coûts humains associés à un développement économique rapide et non réglementé. Elle souligne l'importance de politiques équilibrées qui favorisent la croissance tout en protégeant la santé et le bien-être des citoyens.
Les origines du syndicalisme remontent à l'époque de la révolution industrielle, une période marquée par une transformation radicale des conditions de travail. Face à des journées laborieuses, prolongées, et souvent dans des environnements dangereux ou insalubres, les travailleurs ont commencé à s'unir pour défendre leurs intérêts communs. Ces premiers syndicats, fréquemment contraints d'opérer dans la clandestinité en raison de législations restrictives et d'une forte opposition patronale, se sont érigés en champions de la cause ouvrière, avec pour objectif l'amélioration concrète des conditions de vie et de travail de leurs membres. La lutte syndicale s'est articulée autour de plusieurs axes fondamentaux. Premièrement, la réduction des horaires de travail excessifs et l'amélioration des conditions d'hygiène en milieu industriel étaient des revendications centrales. Deuxièmement, les syndicats se sont battus pour obtenir des salaires permettant non seulement de survivre mais aussi de vivre avec un minimum de confort. En outre, ils se sont efforcés d'assurer une certaine stabilité de l'emploi, protégeant ainsi les ouvriers des licenciements arbitraires et des risques professionnels évitables. Enfin, les syndicats ont lutté pour la reconnaissance de droits fondamentaux, tels que la liberté d'association et le droit de grève. Malgré l'adversité et les résistances, ces mouvements ont peu à peu obtenu des avancées législatives qui ont commencé à réguler le monde du travail, posant les jalons d'une amélioration progressive des conditions laborieuses de l'époque. Ainsi, les premiers syndicats ont non seulement façonné le paysage social et économique de leur temps, mais ont également préparé le terrain pour le développement des organisations syndicales contemporaines, acteurs toujours influents dans la défense des droits des travailleurs à travers le monde.
La faible mortalité adulte dans les villes industrielles, en dépit de conditions de vie précaires, peut s'expliquer par un phénomène de sélection naturelle et sociale. Les ouvriers migrants venus des campagnes pour travailler dans les usines étaient souvent ceux qui disposaient de la meilleure santé et de la plus grande résilience, qualités nécessaires pour entreprendre un tel changement de vie et supporter les rigueurs du travail industriel. Ces adultes, donc, représentaient un sous-ensemble de la population rurale caractérisé par une plus grande force physique et une audace supérieure à la moyenne. Ces traits étaient avantageux pour survivre dans un milieu urbain où les conditions de travail étaient dures et les risques sanitaires élevés. Par contre, les enfants et les jeunes, plus vulnérables de par leur développement incomplet et leur manque d'immunité face aux maladies urbaines, souffraient davantage et étaient donc plus susceptibles de succomber prématurément. D'un autre côté, les adultes qui survivaient aux premières années de travail en ville pouvaient développer une certaine résistance aux conditions de vie urbaines. Cela ne veut pas dire qu'ils ne souffraient pas des effets néfastes de l'environnement insalubre et des exigences épuisantes du travail en usine ; mais leur capacité à persévérer malgré ces défis se traduisait par une mortalité relativement faible par rapport aux jeunes populations plus fragiles. Cette dynamique est un exemple de la façon dont les facteurs sociaux et environnementaux peuvent influencer les schémas de mortalité au sein d'une population. Cela met aussi en lumière la nécessité des réformes sociales et de l'amélioration des conditions de travail, particulièrement pour protéger les segments les plus vulnérables de la société, notamment les enfants.
L’environnement plus que le travail
L'observation que l'environnement a eu un impact meurtrier plus important que le travail lui-même pendant la révolution industrielle met en évidence les conditions extrêmes dans lesquelles vivaient les travailleurs de l'époque. Bien que le travail en usine ait été extrêmement difficile, avec de longues heures, un travail répétitif et dangereux, et peu de mesures de sécurité, c'est souvent l'environnement domestique et urbain qui a été le plus létal. Les conditions de logement insalubres, caractérisées par une surpopulation, un manque de ventilation, une faible ou aucune infrastructure d'élimination des déchets et des systèmes d'égout déficients, ont conduit à des taux élevés de maladies contagieuses. Des maladies comme le choléra, la tuberculose, et la typhoïde se répandaient rapidement dans ces conditions. En outre, la pollution de l'air due à la combustion de charbon dans les usines et les foyers a contribué à des problèmes respiratoires et à d'autres problèmes de santé. Les rues étroites et surpeuplées, l'absence de zones vertes et d'espaces publics propres, et l'accès limité à de l'eau potable propre exacerbèrent les problèmes de santé publique. L'impact de ces conditions environnementales délétères était souvent immédiat et visible, menant à des épidémies et des taux de mortalité élevés, particulièrement chez les enfants et les personnes âgées, qui étaient moins capables de résister aux maladies. Cela a mis en évidence le besoin critique de réformes sanitaires et environnementales, telles que l'amélioration de l'habitat, l'introduction de lois sur la santé publique, et la création d'infrastructures d'assainissement, pour améliorer la qualité de vie et la santé des populations urbaines.
La loi Le Chapelier, du nom de l'avocat et homme politique français Isaac Le Chapelier qui la proposa, est une loi emblématique de l'époque post-révolutionnaire en France. Promulguée en 1791, cette loi visait à supprimer les corporations de l'Ancien Régime ainsi que toute forme d'associations professionnelles ou de groupements d'ouvriers et d'artisans. Le contexte historique est important pour comprendre les motifs de cette loi. La Révolution française avait comme l'un de ses objectifs la destruction des structures féodales et des privilèges, y compris ceux liés aux guildes et aux corporations, qui contrôlaient l'accès aux métiers et pouvaient fixer les prix et les normes de production. Dans cet esprit d'abolition des privilèges, la loi Le Chapelier visait à libéraliser le travail et à promouvoir une forme d'égalité devant le marché. La loi interdisait aussi les coalitions, c'est-à-dire les ententes entre ouvriers ou employeurs pour fixer les salaires ou les prix. En ce sens, elle s'opposait aux premiers mouvements de solidarité ouvrière qui pouvaient menacer la liberté du commerce et de l'industrie prônée par les révolutionnaires. Cependant, en interdisant toute forme d'association entre ouvriers, la loi a également eu pour effet de limiter sévèrement la capacité des travailleurs à défendre leurs intérêts et à améliorer leurs conditions de travail. Les syndicats ne se développeront légalement en France qu'à partir de la loi Waldeck-Rousseau en 1884, qui revient sur l'interdiction des coalitions ouvrières et autorise la création de syndicats.
L'immigration vers les bassins industriels au XIXe siècle fut souvent un phénomène de sélection naturelle où les plus robustes et les plus aventureux quittaient leurs campagnes natales pour chercher de meilleures opportunités économiques. Ces individus, par leur constitution plus solide, avaient une espérance de vie un peu supérieure à celle de la moyenne, malgré les conditions de travail extrêmes et l'usure physique prématurée qu'ils subissaient dans les usines et les mines. La vieillesse précoce était une conséquence directe de la pénibilité du travail industriel. La fatigue chronique, les maladies professionnelles, et l'exposition à des conditions dangereuses faisaient que les travailleurs "vieillissaient" plus vite physiquement et souffraient de problèmes de santé qui s'apparentent normalement à ceux de personnes plus âgées. Pour les enfants des familles ouvrières, la situation était encore plus tragique. Leur vulnérabilité aux maladies, accentuée par des conditions sanitaires déplorables, augmentait dramatiquement le risque de mortalité infantile. La contamination de l'eau potable était une cause majeure de maladies telles que la dysenterie et le choléra, qui entraînaient déshydratation et diarrhées mortelles, particulièrement chez les jeunes enfants. De plus, la conservation des aliments était un problème majeur. Les produits frais comme le lait, qui devaient être transportés depuis la campagne jusqu'aux villes, se détérioraient rapidement sans les techniques de réfrigération modernes, exposant les consommateurs à des risques d'intoxication alimentaire. Cela était particulièrement dangereux pour les enfants, dont le système immunitaire en développement les rendait moins résistants aux infections alimentaires. Ainsi, malgré la robustesse des adultes migrants, les conditions environnementales et professionnelles dans les zones industrielles contribuaient à un taux de mortalité élevé, en particulier parmi les populations les plus vulnérables telles que les enfants.
Les épidémies de choléra
Le choléra est un exemple frappant de la façon dont les maladies infectieuses peuvent se propager à l'échelle mondiale, favorisées par les mouvements de population et le commerce international. Au XIXe siècle, les pandémies de choléra ont illustré la connectivité croissante du monde, mais aussi les limites de la compréhension médicale et de la santé publique de l'époque. La propagation du choléra a commencé avec la colonisation britannique en Inde. La maladie, qui est causée par la bactérie Vibrio cholerae, a été transportée par des navires marchands et des mouvements de troupes, suivant les grandes routes commerciales et militaires de l'époque. L'accroissement des échanges internationaux et la densification des réseaux de transport ont permis au choléra de s'étendre rapidement à travers le monde. Entre 1840 et 1855, lors de la première pandémie mondiale de choléra, la maladie a suivi un itinéraire depuis l'Inde vers d'autres parties de l'Asie, la Russie, et finalement l'Europe et les Amériques. Ces pandémies ont frappé des villes entières, entraînant des morts massives et exacerbant la peur et la stigmatisation des étrangers, en particulier ceux d'origine asiatique, perçus à l'époque comme les vecteurs de la maladie. Cette stigmatisation a été alimentée par des sentiments de supériorité culturelle et des notions de « barbarie » attribuées aux sociétés non européennes. En Europe, ces idées ont souvent été utilisées pour justifier le colonialisme et les politiques impérialistes, en se basant sur l'argument que les Européens apportaient la « civilisation » et la « modernité » à des parties du monde considérées comme arriérées ou barbares. Le choléra a également stimulé des avancées importantes dans le domaine de la santé publique. Par exemple, c'est en étudiant les épidémies de choléra que le médecin britannique John Snow a pu démontrer, dans les années 1850, que la maladie se propageait par l'eau contaminée, une découverte qui a conduit à des améliorations significatives dans les systèmes d'eau potable et d'assainissement.
La croissance économique et les changements sociaux en Europe durant le XIXe siècle ont été accompagnés de peurs et d'incertitudes quant aux conséquences de la modernisation. Avec l'urbanisation rapide, l'essor de la densité de population dans les villes et les conditions souvent insalubres, les sociétés européennes ont été confrontées à de nouveaux risques sanitaires. La théorie selon laquelle la modernité permettait aux individus « faibles » de survivre était largement répandue et reflétait une compréhension du monde influencée par les idées darwiniennes de survie des plus aptes. Cette perspective a renforcé les craintes d'une possible « dégénérescence » de la population si les maladies infectieuses devaient se répandre parmi ceux qui étaient jugés moins résistants. La médiatisation des épidémies a joué un rôle crucial dans la perception publique des risques sanitaires. Les nouvelles de l'arrivée du choléra ou des premières victimes de la maladie dans une ville particulière étaient souvent accompagnées d'un sentiment d'urgence et d'angoisse. Les journaux et les feuilles volantes de l'époque diffusaient ces informations, exacerbant la peur et parfois la panique au sein de la population. La maladie a également mis en évidence les inégalités sociales criantes. Le choléra frappait de manière disproportionnée les pauvres, qui vivaient dans des conditions plus précaires et n'avaient pas les moyens d'assurer une bonne hygiène ou de se procurer une alimentation adéquate. Cette différence de mortalité entre les classes sociales a souligné l'importance des déterminants sociaux de la santé. Quant à la résistance au choléra grâce à une alimentation riche, l'idée que les acides gastriques tuent le virus du choléra est partiellement vraie dans le sens où un pH gastrique normal est un facteur de défense contre la colonisation par le vibrio cholerae. Cependant, ce n'est pas une question de consommation de viande versus pain et pommes de terre. En réalité, les personnes qui souffraient de malnutrition ou de faim étaient plus vulnérables aux maladies, car leur système immunitaire était affaibli et leurs défenses naturelles contre les infections étaient moins efficaces. Il est important de souligner que le choléra n'est pas causé par un virus, mais par une bactérie, et que la survie du micro-organisme dans l'estomac dépend de divers facteurs, y compris la charge infectieuse ingérée et l'état de santé général de la personne. Ces épidémies ont forcé les gouvernements et les sociétés à porter une attention accrue à la santé publique, menant à des investissements dans l'amélioration des conditions de vie, l'assainissement et les infrastructures d'eau potable, et finalement à la réduction de l'impact de telles maladies.
Les grandes épidémies qui ont frappé la France et d'autres parties de l'Europe après les révolutions de 1830 et 1848 ont eu lieu dans un contexte de profonds bouleversements politiques et sociaux. Ces maladies ravageuses ont souvent été perçues par les classes défavorisées comme des fléaux exacerbés, voire provoqués, par les conditions de vie misérables dans lesquelles elles étaient contraintes de vivre, souvent à proximité des centres urbains en pleine expansion et industrialisation. Dans un tel climat, il n'est pas surprenant que la suspicion et la colère des classes laborieuses se soient dirigées contre la bourgeoisie, accusée de négligence, voire de malveillance. Les théories du complot telles que l'accusation selon laquelle les bourgeois cherchaient à "empoisonner" ou à réprimer la "fureur populaire" par le biais de maladies ont pu trouver un écho dans une population désespérée et cherchant des explications à sa souffrance. En Russie, sous le règne du tsar, des manifestations déclenchées par la détresse provoquée par des épidémies ont été réprimées par l'armée. Ces événements reflètent la tendance des autorités de l'époque à répondre par la force aux troubles sociaux, souvent sans adresser les causes profondes du mécontentement, comme la pauvreté, l'insécurité sanitaire et le manque d'accès aux services de base. Ces épidémies ont mis en évidence les liens entre les conditions de santé et les structures sociales et politiques. Elles ont montré que les problèmes de santé publique ne pouvaient être dissociés des conditions de vie des populations, en particulier de celles des classes les plus démunies. Face à ces crises sanitaires, la pression montait sur les gouvernements pour qu'ils améliorent les conditions de vie, investissent dans des infrastructures sanitaires et mettent en place des politiques de santé publique plus efficaces. Ces périodes d'épidémies ont donc également joué un rôle catalyseur dans l'évolution de la pensée politique et sociale, soulignant la nécessité d'une plus grande égalité et d'une meilleure prise en charge des citoyens par les États.
Les médecins du XIXe siècle se trouvaient souvent au cœur des crises sanitaires, agissant en tant que figures de confiance et de savoir. Ils étaient perçus comme des piliers de la communauté, notamment en raison de leur engagement auprès des malades et de leur formation scientifique, acquise dans des établissements d'enseignement supérieur. Ces professionnels de la santé avaient une grande influence et leur conseil était généralement respecté par la population. Avant que Louis Pasteur ne révolutionne la médecine avec la théorie des germes en 1885, la compréhension des maladies infectieuses était très limitée. Les médecins de l'époque ne connaissaient pas l'existence des virus et des bactéries comme agents pathogènes. Malgré cela, ils n'étaient pas pour autant dénués de logique ou de méthode dans leur pratique. Lorsqu'ils étaient confrontés à des maladies telles que le choléra, les médecins utilisaient les connaissances et les techniques disponibles à l'époque. Par exemple, ils observaient attentivement l'évolution des symptômes et adaptaient leur traitement en conséquence. Ils essayaient de réchauffer les patients durant la phase "froide" du choléra, caractérisée par une peau froide et bleuâtre due à la déshydratation et à la baisse de la circulation sanguine. Ils s'efforçaient aussi de fortifier le corps avant l'arrivée de la "dernière phase" de la maladie, souvent marquée par une extrême faiblesse, qui pouvait conduire à la mort. Les médecins utilisaient également des méthodes telles que la saignée ou les purges, qui étaient fondées sur des théories médicales de l'époque mais qui sont aujourd'hui considérées comme non efficaces voire nuisibles. Cependant, malgré les limitations de leur pratique, leur dévouement à soigner et à observer avec rigueur les effets de leurs traitements témoignait de leur volonté de combattre la maladie avec les outils dont ils disposaient. L'approche empirique des médecins de cette époque a contribué à l'accumulation des connaissances médicales qui, par la suite, ont été transformées et affinées avec l'avènement de la microbiologie et d'autres sciences médicales modernes.
Georges-Eugène Haussmann, connu sous le nom de Baron Haussmann, a orchestré une transformation radicale de Paris sous le Second Empire, sous le règne de Napoléon III. Sa tâche était de remédier aux problèmes pressants de la capitale française, qui souffrait d'une surpopulation extrême, de conditions sanitaires déplorables et d'un enchevêtrement de ruelles issues du Moyen Âge qui ne répondaient plus aux besoins de la ville moderne. La stratégie d'Haussmann pour revitaliser Paris était globale. Il a d'abord pris des mesures pour assainir la ville. Avant ses réformes, Paris luttait contre des fléaux tels que le choléra, exacerbés par des rues étroites et un système d'égouts déficient. Il a introduit un système d'égouts innovant qui a considérablement amélioré la santé publique. Ensuite, Haussmann s'est concentré sur l'amélioration des infrastructures en établissant un réseau de larges avenues et de boulevards. Ces nouvelles voies n'étaient pas seulement esthétiques mais fonctionnelles, améliorant la circulation de l'air et de la lumière et facilitant les déplacements. En parallèle, Haussmann a repensé l'urbanisme de la ville. Il a créé des espaces harmonieux avec des parcs, des places et des alignements de façades, qui ont donné à Paris son aspect caractéristique que nous connaissons aujourd'hui. Toutefois, ce processus a eu des répercussions sociales importantes, notamment le déplacement des populations les plus pauvres vers la périphérie. Les travaux de rénovation ont conduit à la destruction de nombreux petits commerces et habitations précaires, poussant ainsi les classes défavorisées à s'installer en banlieue. Ces changements ont provoqué des réactions mitigées parmi les Parisiens de l'époque. Alors que la bourgeoisie pouvait craindre les troubles sociaux et voyait avec appréhension la présence de ce qu'elle considérait comme des "classes dangereuses", l'ambition d'Haussmann était également de rendre la ville plus attrayante, plus sûre et mieux adaptée à l'époque. Néanmoins, le coût et les conséquences sociales des travaux d'Haussmann ont été source de controverses et de débats politiques intenses.
La « question sociale »
Au cours du XIXe siècle, avec l'ascension du capitalisme industriel, les structures sociales subissent des changements radicaux, déplaçant l'ancienne hiérarchie basée sur la noblesse et le sang par une hiérarchie axée sur le statut social et la richesse. Une nouvelle élite bourgeoise émerge, composée d'individus qui, ayant réussi dans le monde des affaires, acquièrent la richesse et le crédit social jugés nécessaires pour gouverner le pays. Cette élite représente une minorité qui, pour un temps, détient le monopole du droit de vote, étant considérée comme la plus apte à prendre des décisions pour le bien de la nation. Les ouvriers, en revanche, sont souvent perçus de manière paternaliste, comme des enfants incapables de gérer leurs propres affaires ou de résister aux tentations de l'ivresse et d'autres vices. Cette vision est renforcée par les théories morales et sociales de l'époque qui mettent l'accent sur la tempérance et la responsabilité individuelle. La peur du choléra, une maladie épouvantable et mal comprise, alimente un ensemble de croyances populaires, y compris l'idée que le stress ou la colère pourraient induire la maladie. Cette croyance a contribué à un calme relatif dans les classes ouvrières, qui se méfiaient des émotions fortes et de leur potentiel à engendrer des fléaux. En l'absence d'une compréhension scientifique des causes de telles maladies, les théories abondent, certaines relevant du mythe ou de la superstition. Dans cet environnement, la bourgeoisie développe une forme de paranoïa à l'égard des banlieues ouvrières. Les périphéries urbaines, souvent surpeuplées et insalubres, sont vues comme des foyers de maladie et de désordre, menaçant la stabilité et la propreté des centres urbains plus aseptisés. Cette crainte est accentuée par le contraste entre les conditions de vie de l'élite bourgeoise et celles des ouvriers, ainsi que par la menace perçue que représentent les rassemblements et les révoltes populaires pour l'ordre établi.
Buret était un observateur attentif des conditions de vie de la classe ouvrière au XIXe siècle, et son analyse reflète les inquiétudes et les critiques sociales de cette époque marquée par la Révolution industrielle et l'urbanisation rapide : « Si vous osez pénétrer dans les quartiers maudits où [la population ouvrière] habite, vous verrez à chaque pas des hommes et des femmes flétries par le vice et par la misère, des enfants à demi nus qui pourrissent dans la saleté et étouffent dans des réduits sans jour et sans air. Là, au foyer de la civilisation, vous rencontrerez des milliers d’hommes retombés, à force d’abrutissement, dans la vie sauvage ; là, enfin, vous apercevrez la misère sous un aspect si horrible qu’elle vous inspirera plus de dégoût que de pitié, et que vous serez tenté de la regarder comme le juste châtiment d’un crime [...]. Isolés de la nation, mis en dehors de la communauté sociale et politique, seuls avec leurs besoins et leurs misères, ils s’agitent pour sortir de cette effrayante solitude, et, comme les barbares auxquels on les a comparés, ils méditent peut-être une invasion. »
La force de cette citation réside dans sa description graphique et émotionnelle de la pauvreté et de la dégradation humaine dans les quartiers ouvriers des villes industrielles. Buret utilise une imagerie choquante pour susciter une réaction chez le lecteur, dépeignant des scènes de dégradation qui sont en contraste frappant avec l'idéal de progrès et de civilisation porté par l'époque. En qualifiant les quartiers ouvriers de "maudits" et en évoquant des images d'hommes et de femmes "flétries par le vice et par la misère", il attire l'attention sur les conditions inhumaines engendrées par le système économique de l'époque. La référence aux "enfants à demi nus qui pourrissent dans la saleté" est particulièrement poignante et reflète une réalité sociale cruelle où les plus vulnérables, les enfants, sont les premières victimes de l'industrialisation. La mention des "réduits sans jour et sans air" rappelle les logements insalubres et surpeuplés dans lesquels étaient entassées les familles ouvrières. Buret souligne également l'isolement et l'exclusion des ouvriers de la communauté politique et sociale, suggérant que, privés de reconnaissance et de droits, ils pourraient devenir une force subversive, comparés à des "barbares" méditant une "invasion". Cette métaphore de l'invasion suggère une peur de la révolte ouvrière parmi les classes dirigeantes, craignant que la détresse et l'agitation des ouvriers ne se transforment en une menace pour l'ordre social et économique. Dans son contexte historique, cette citation illustre les tensions sociales profondes du XIXe siècle et offre un commentaire cinglant sur les conséquences humaines de la modernité industrielle. Elle invite à la réflexion sur la nécessité d'une intégration sociale et d'une réforme politique, reconnaissant que le progrès économique ne peut être déconnecté du bien-être et de la dignité de tous les membres de la société.