« The monetary system » : différence entre les versions
Aucun résumé des modifications |
|||
| (6 versions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 2 : | Ligne 2 : | ||
| image = | | image = | ||
| image_caption = | | image_caption = | ||
| cours = [[Introduction | | cours = [[Introduction to Macroeconomics]] | ||
| faculté = | | faculté = | ||
| département = | | département = | ||
| professeurs = | | professeurs = | ||
*[[Federica Sbergami|Sbergami, Federica]]<ref>[https://www.unige.ch/gsem/en/research/faculty/all/federica-sbergami/ Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur le site de l'Université de Genève]</ref><ref>[https://www.unine.ch/irene/home/equipe/federica_sbergami.html Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur le site de l'Université de Neuchâtel]</ref><ref>[https://www.researchgate.net/scientific-contributions/14836393_Federica_Sbergami Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur Research Gate]</ref> | *[[Federica Sbergami|Sbergami, Federica]]<ref>[https://www.unige.ch/gsem/en/research/faculty/all/federica-sbergami/ Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur le site de l'Université de Genève]</ref><ref>[https://www.unine.ch/irene/home/equipe/federica_sbergami.html Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur le site de l'Université de Neuchâtel]</ref><ref>[https://www.researchgate.net/scientific-contributions/14836393_Federica_Sbergami Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur Research Gate]</ref> | ||
*[[Nicolas Maystre]]<ref>Researchgate.net - [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nicolas_Maystre Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>Google Scholar - [https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=B73U0wsAAAAJ&hl=en Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>VOX, CEPR Policy Portal - [https://voxeu.org/users/nicolasmaystre0 Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>[http://nicolas.maystre.ch/ Nicolas Maystre's webpage]</ref><ref>Cairn. | *[[Nicolas Maystre]]<ref>Researchgate.net - [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nicolas_Maystre Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>Google Scholar - [https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=B73U0wsAAAAJ&hl=en Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>VOX, CEPR Policy Portal - [https://voxeu.org/users/nicolasmaystre0 Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>[http://nicolas.maystre.ch/ Nicolas Maystre's webpage]</ref><ref>Cairn.info - [https://www.cairn.info/publications-de-Nicolas-Maystre--104530.htm Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>Linkedin - [https://www.linkedin.com/in/nicolas-maystre-82660737/?originalSubdomain=ch Nicolas Maystre]</ref><ref>Academia.edu - [https://unctad.academia.edu/NicolasMaystre Nicolas Maystre]</ref> | ||
| enregistrement = | | enregistrement = | ||
| lectures = | | lectures = | ||
*[[ | *[[Introductory aspects of macroeconomics]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Gross Domestic Product (GDP)]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Consumer Price Index (CPI)]] | ||
*[[Production | *[[Production and economic growth]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Unemployment]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Financial Market]] | ||
*[[ | *[[The monetary system]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Monetary growth and inflation]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Open Macroeconomics: Basic Concepts]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Open Macroeconomics: the Exchange Rate]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Equilibrium in an open economy]] | ||
*[[ | *[[The Keynesian approach and the IS-LM model]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Aggregate demand and supply]] | ||
*[[ | *[[The impact of monetary and fiscal policies]] | ||
*[[Trade-off | *[[Trade-off between inflation and unemployment]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Response to the 2008 Financial Crisis and International Cooperation]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Translations | {{Translations | ||
| fr = Le système monétaire | | fr = Le système monétaire | ||
| es = | | es = El sistema monetario | ||
}} | }} | ||
= Types of currency = | = Types of currency = | ||
| Ligne 176 : | Ligne 175 : | ||
== The Credit Multiplication Mechanism == | == The Credit Multiplication Mechanism == | ||
1. | 1. Banks are assumed to have only sight deposits and the amount of reserves covers their holdings of cash and giro accounts. Furthermore, in the initial situation, the bank <math>A</math> has no excess reserves. Furthermore, the reserve requirement ratio, r = 20%. | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 1.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 1.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
2. | 2. Now suppose that the central bank decides to increase the monetary base by repurchasing securities from the bank <math>A</math> (for an amount of 100) and credits the giro accounts of the bank <math>A</math> as a counterpart. | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 2.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 2.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
3. | 3. The bank <math>A</math> uses its surplus reserves to make new loans (for an amount of 100). This has two consequences: | ||
:a) | :a) The granting of loans leads to new deposits (by hypothesis, there is no transformation of scriptural money into cash at the moment). | ||
:b) | :b) The creation of new deposits requires an increase in reserve requirements. | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 3.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 3.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
4. | 4. The remainder of the excess reserves give rise to new loans amounting to 80. Again, there is no loss of reserves, but the creation of money and the transformation of excess reserves into required reserves. | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 4.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 4.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
5. | 5. The process may continue until there are no more excess reserves, i.e. until all initial excess reserves have been transformed into required reserves. The result is : | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 5.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 5.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
Total money supply (maximum) <math display="block">= 100 + 80 + 64 + 51.2 + ... = 100 [1+(1-0.2)+(1-0.2)2+(1-0.2)3+...] = \lim_{n \to \infty}\sum_{i=0}^n 100 \times (1 - 0.2)^i = \frac {100}{1 - (1 - 0.2)} = \frac {100}{0.2} = 500</math> | |||
In total, 500 scriptural money was created, for 100 percent of the excess reserves that initially appeared. The credit multiplier is therefore equal to 5. | |||
The credit multiplier is defined as the ratio between the total change in credits, ΔCR, and the initial change in excess reserves, ΔiRE. | |||
:<math>m_c = \frac {\Delta CR}{\Delta_iRE}</math> | :<math>m_c = \frac {\Delta CR}{\Delta_iRE}</math> | ||
Assuming that there are no 'leakages' from the credit multiplier circuit, i.e. that the private sector does not seek to convert part of the newly created book money into fiat money. The credit multiplier is the inverse of the reserve requirement ratio. (<math display="inline">r</math>): | |||
:<math display="block">m_c = \frac{1}{r}</math> | :<math display="block">m_c = \frac{1}{r}</math> | ||
In the example: <math>r = 20% = 0.2 = \frac{1}{5}</math> => <math>m = 5</math>. Si <math>r = 0.1</math>, <math>m = 10</math>. | |||
There are several ways to demonstrate that <math>m_c = \frac {1}{r}</math>. The simplest is to point out that <math>\Delta_iRE = \Delta RO</math>. Or <math>\Delta RO = r</math>· <math>\Delta DV = r \times \Delta CR</math>. Therefore, | |||
:<math>m_c = \frac {\Delta CR}{r \times \Delta CR} = \frac {1}{r}</math> | :<math>m_c = \frac {\Delta CR}{r \times \Delta CR} = \frac {1}{r}</math> | ||
In general: <math> M = \frac {1}{r} \times H = m \times H</math> | |||
== | == The Money Multiplier: full version == | ||
Exemple (Same same but different!) | Exemple (Same same but different!) | ||
1. | 1. Same assumption as above, that we abandon the assumption that agents in the non-bank sector do not seek to exchange some of the newly created book money for cash. In this case, when the bank makes a loan, it must expect that the cash-in-transaction money created in return will be exchanged for cash. This means that the bank will have to draw on its excess reserves to provide the requested cash. Excess reserves will decline more rapidly, because of this leakage out of the credit multiplier circuit, and the credit multiplier will therefore be lower. | ||
Let us call <math>c</math> the leakage coefficient, i.e. the share of new credits converted into cash: | |||
:::<math>c = \frac{\Delta N_p}{\Delta CR}</math> | :::<math>c = \frac{\Delta N_p}{\Delta CR}</math> | ||
| Ligne 233 : | Ligne 232 : | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 7.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 7.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
3’. | 3’. Bank A uses its excess reserves to make new loans (for an amount of 100). However, the non-bank sector wants to keep half of it in cash: Assumption: <math>c = 50%</math>. | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 8.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 8.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
4’. | 4’. The remaining excess reserves give rise to new loans for an amount of 40. | ||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 9.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 9.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
5’. | |||
5’. The process can continue until there are no more excess reserves. The result is : | |||
[[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 10.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | [[Fichier:Mécanisme de multiplication des crédits 10.png|400px|vignette|centré]] | ||
In its full version (with leakage), the credit multiplier becomes : | |||
:<math>m_c = \frac{\Delta CR}{\Delta_iRE} = \frac {1}{(r+c-rc}</math> | :<math>m_c = \frac{\Delta CR}{\Delta_iRE} = \frac {1}{(r+c-rc}</math> | ||
Evidence: | |||
:<math>\Delta_iRE = \Delta RO + \Delta N_p</math> | :<math>\Delta_iRE = \Delta RO + \Delta N_p</math> | ||
Because the process stops when mandatory stockpiling and leakage has exhausted the initial surplus reserves. Replacing the increase in reserve requirements and requests for conversion to cash with their respective values has: | |||
:<math>\Delta_iRE= r \times \Delta DV + c \times \Delta CR</math> (car <math>\Delta RO = r \Delta DV</math> et <math>= \Delta N_p = c \Delta CR</math>) | :<math>\Delta_iRE= r \times \Delta DV + c \times \Delta CR</math> (car <math>\Delta RO = r \Delta DV</math> et <math>= \Delta N_p = c \Delta CR</math>) | ||
| Ligne 257 : | Ligne 257 : | ||
:<math>= \Delta CR [ c + r (1-c)]</math> | :<math>= \Delta CR [ c + r (1-c)]</math> | ||
From then on: | |||
:<math>\frac {\Delta CR}{\Delta_iRE} = \frac {1}{r + c - rc}</math> | :<math>\frac {\Delta CR}{\Delta_iRE} = \frac {1}{r + c - rc}</math> | ||
== | == BC's control instruments == | ||
''' | '''Open market operations''': as already mentioned, central banks can intervene in asset markets. When a CB buys (sells) government bonds the amount of money in circulation increases (decreases). | ||
'''Modification | '''Modification of the reserve ratio''': if the minimum fraction of deposits that must be kept as reserves increases (decrease), the quantity of money in circulation decreases (increases). NB: Traditionally, central banks have used this measure only very rarely, except in China in recent years. Examples: 10% USA, 20% CH, nothing UK, nothing Australia... | ||
''' | '''Change in the discount rate''' (or key rate): commercial banks borrow money from the central bank when their reserves are too low in relation to the reserve requirement. If the discount rate ↑ (↓) ⇒ the money supply ↓ (↑). Most central banks have lowered this rate since the beginning of the last financial crisis. Today the key rates are extremely low. | ||
== | == Effectiveness of the central bank's control of the money supply == | ||
Central banks exercise only partial control over the supply of money. In particular, central banks cannot control : | |||
* | *the amount of deposits that households decide to convert into hard currency (leakage from the credit cycle). In this case, if private agents hold in cash a percentage <math>c</math> of the deposits, the multiplier becomes <math>m = \frac {1}{r + c}</math>, a good approximation of the true multiplier <math>m = \frac {1}{r + c - rc}</math> if <math>r</math> and <math>c</math> are small. | ||
* | *the aggregate amount of loans made by commercial banks. | ||
In summary, since the amount of money in circulation in the economy depends in part on the behaviour of bankers and depositors, central bank control can only be imperfect. | |||
In the following we will assume that the central bank perfectly controls the supply of money. | |||
= | = Summary = | ||
The term money refers to all assets used by households to purchase goods and services. | |||
Currency has three functions: exchange intermediary, unit of account, store of value, etc. | |||
Commodity money is money that has an intrinsic value. | |||
Currency has no intrinsic value. | |||
The central bank controls the supply of money through open market operations by changing the reserve requirement ratio, changing the discount rate, etc. | |||
The central bank cannot control the amount of loans granted by commercial banks or the deposit decisions of households. As a result, the central bank's control over the money supply is only partial. | |||
Some causes of inflation (= increase in the general price level) are related to the determinants of the demand (next chapter) and supply (this chapter) of money. | |||
= Annexes = | = Annexes = | ||
Version actuelle datée du 3 avril 2020 à 10:54
| Professeur(s) | |
|---|---|
| Cours | Introduction to Macroeconomics |
Lectures
- Introductory aspects of macroeconomics
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Production and economic growth
- Unemployment
- Financial Market
- The monetary system
- Monetary growth and inflation
- Open Macroeconomics: Basic Concepts
- Open Macroeconomics: the Exchange Rate
- Equilibrium in an open economy
- The Keynesian approach and the IS-LM model
- Aggregate demand and supply
- The impact of monetary and fiscal policies
- Trade-off between inflation and unemployment
- Response to the 2008 Financial Crisis and International Cooperation
Types of currency[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The functions of money[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
Currency is the stock of assets that can be readily mobilized for transactions.
Beware of common parlance:
- "Have money" or "pay in cash" refers to cash. Around 10% of money is made up of cash.
- "Having money" or "earning a lot of money" refers to wealth or income. However, money is not wealth (assets or fortune) nor is it income.
It essentially has three functions:
- Reserve value (money is a means of transferring purchasing power from the present to the future).
- Unit of account (the unit of account by which economic transactions are measured).
- Intermediary of exchange (means used to purchase goods and services). In a barter economy, exchange requires the double coincidence of needs and economic agents can carry out only simple transactions. Money makes more indirect exchanges possible and reduces transaction costs.
Liquidity: the ease with which an asset can be converted into the medium of exchange of the economic system. Currency = the most liquid asset of all.
Types of currency[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
Money can be seen as a good with important positive externalities. The more people who accept it, the more useful it is for each individual.
Commodity money: most societies of the past used one or the other good with an intrinsic value (example: gold, but also camels, furs, salt... as the case may be).
'Fiduciary money (or fiat money): (Tangible) money devoid of any intrinsic value and which owes its status as money to the fact that the State has conferred legal tender on it (all metal coins and banknotes in circulation).
scriptural money: intangible money, represented by an accounting entry that can be transformed into fiduciary money at any time (all assets held at the bank or post office).
NB: Credit cards are simple media allowing the transfer of scriptural money over time.
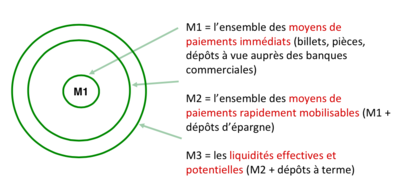
Monetary aggregates[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
How is currency measured? Four types of monetary aggregates :
Normally "money" is understood to mean the aggregate M1. M0 (or, hereafter, H) is also referred to as the monetary base.
Monetary aggregates: euro area[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
Central banks and the money supply[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
History of money and banking[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The history of money is intimately linked to that of the banks (see video).
From the XVIth-XVIIth century :
- Depositing gold with a goldsmith to protect it from theft → received.
- Use of receipts as a means of payment (beginning of fiat money).
- Loan of gold on deposit against interest → goldsmiths become bankers.
- For each gold bullion, issuing several notes → confidence in the repayment ability of the goldsmiths-bankers → reserves.
- Increase of reserves against the risk of bankruptcies and creation of national banks controlling the issue of banknotes which were granted legal tender status.
Until the First World War metal banknotes were convertible at the issuing institute at a rate established by the central bank (gold standard system). Convertibility was abandoned in the 1920s (coins and banknotes have a value conferred on them by general agreement, but no intrinsic value and they can no longer be exchanged for gold).
The role of central banks[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
In most countries, the quantity of money available (money supply) is controlled by the state and its supervision is delegated to an institution more or less independent of political power: the central bank. Central banks:
- (i)supervise the banking system and
- (ii) ensure the stability of the monetary system by regulating the quantity of money in circulation in the economy and thereby influencing interest rates and sometimes the exchange rate.
These instruments may affect inflation and the levels of output and employment in the short term, as will be discussed in the following chapters.
The set of actions put in place by the central bank to influence the money supply and to supervise the proper functioning of the monetary system constitutes monetary policy.
The European Central Bank and the Eurosystem[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The European Central Bank (ECB), located in Frankfurt, Germany, was created on June 1, 1998 by the 12 European countries (then 11, now 17) that make up the European Monetary Union, i.e. the 12 countries that have decided to adopt a single currency (the euro) and a common monetary policy.
The ECB and all the central banks of the European Union Member States that have adopted the euro make up the Eurosystem.
The main objective of the ECB is to promote financial and price stability in order to ensure non-inflationary growth.
The ECB is supposed to be independent of political power.
The Bank of England and the Federal Reserve[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom. Established in 1694, it obtained independence in interest rate management only in 1997. As with the ECB, the main objective of the Bank of England is to promote price stability, but it is the government that defines this objective in concrete terms.
The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States. Created in 1913, the "FED", is composed of a board of governors (of which Ben Bernanke is the president, since 2006), the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), twelve regional banks (Federal Reserve Banks). The FOMC is the committee responsible for monetary policy and is made up of the seven members of the Board of Governors and the twelve presidents of the regional banks (of which only five have voting rights at any given time).
Role of the money supply[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The size of the money supply is expected to change in line with the quantity of transactions taking place on the market, i.e. in line with the development of GDP (= proxy of the volume of transactions).
As will become clearer in the rest of our lecture, when money supply and GDP do not move at the same pace or in the same direction, this is when economic problems (inflation, unemployment) may begin to arise.
Central banks therefore undertake monetary policy actions aimed at influencing the evolution of the money supply. Measuring the money supply therefore enables the BC (Central Bank) to know whether it is necessary to act on the quantity of money available in the economy in the event of imbalances (inflation in particular).
But: the quantity of money in circulation in the economic system is greater than the monetary base, which is directly controlled by the CB () and, to understand its evolution, it is also necessary to analyse the role played by the commercial banks...
Central bank instruments[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
THREE MAIN TOOLS
Central banks govern the amount of currency in circulation in the country through money market interventions (open-market operations), which involve buying or selling government bonds (or other non-monetary assets):
- If selling bonds → reduction of the money supply.
- If buying → bonds, increase the supply of money.
Central banks also control the activities of commercial banks, especially the issuance of book money, by means of the discount rate and the reserve requirement ratio.
The central bank's balance sheet[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The central bank is a true bank of banks: its main customers are commercial banks (and not households or companies): it provides them with banknotes and scriptural money and manages interbank payments on their giro accounts.
Creation of the monetary base[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The monetary base (= asset or liability on the CB's balance sheet) is the currency issued by the central bank (coins and banknotes) + giro accounts. It is directly under the control of the BC.
The central bank exchanges banknotes (or giro account assets) with commercial banks only as a counterpart:
- gold
- of foreign currency (foreign currency)
- of acknowledgements of debt (the bank makes credit)
BC therefore buys gold, foreign currency or securities with its currency (constitution of reserves). It never provides secondary banks with currency without a counterpart. By building up reserves, the BC therefore gives itself the means to recover the currency it has issued at a later date, i.e. either :
- by selling its assets (gold or foreign exchange)
- by getting the loans made to the banks reimbursed...
Constitution of reserves → increase in the supply of money Dissolution of reserves → decrease in the supply of money.
Commercial banks and the supply of money[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The amount of money in circulation is influenced by the central bank's interventions in the asset market and its control over commercial banks and also by the commercial banks' decisions on deposits and loans to their customers.
At any given time commercial banks must hold a certain fraction of the deposits received as reserves and they can lend the rest, thereby creating (scriptural) money → reinjecting money into the system.
The fraction of the amount of deposits that banks are obliged to hold in the form of reserve requirements is the reserve requirement ratio. This coefficient is set by the central bank and can be changed according to the needs of monetary policy. NB: the effective reserve ratio of banks does not necessarily coincide with the reserve requirement ratio (banks may hold more reserves than those imposed by the central bank).
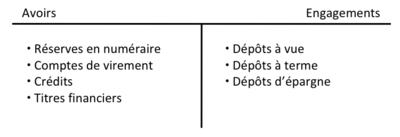
The balance sheet of commercial banks[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The financial position of banks at a given point in time is summarized in their balance sheets. By convention, the assets (assets) are shown on the left side of the balance sheet and the liabilities (liabilities) on the right side.
Bank Money Creation and the Money Multiplier[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The creation of scriptural money is exercised through the mechanism of credit: each time a bank that has excess reserves uses them to make credits, scriptural money is created. In general, the credits in turn give rise to deposits that make it possible to make new credits (once the required reserves have been subtracted) → phenomenon of multiplication of credits and deposits.
The Credit Multiplication Mechanism[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
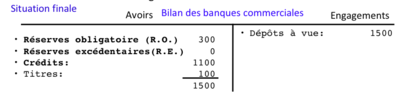
1. Banks are assumed to have only sight deposits and the amount of reserves covers their holdings of cash and giro accounts. Furthermore, in the initial situation, the bank has no excess reserves. Furthermore, the reserve requirement ratio, r = 20%.
2. Now suppose that the central bank decides to increase the monetary base by repurchasing securities from the bank (for an amount of 100) and credits the giro accounts of the bank as a counterpart.
3. The bank uses its surplus reserves to make new loans (for an amount of 100). This has two consequences:
- a) The granting of loans leads to new deposits (by hypothesis, there is no transformation of scriptural money into cash at the moment).
- b) The creation of new deposits requires an increase in reserve requirements.
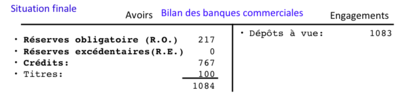
4. The remainder of the excess reserves give rise to new loans amounting to 80. Again, there is no loss of reserves, but the creation of money and the transformation of excess reserves into required reserves.
5. The process may continue until there are no more excess reserves, i.e. until all initial excess reserves have been transformed into required reserves. The result is :
Total money supply (maximum)
In total, 500 scriptural money was created, for 100 percent of the excess reserves that initially appeared. The credit multiplier is therefore equal to 5.
The credit multiplier is defined as the ratio between the total change in credits, ΔCR, and the initial change in excess reserves, ΔiRE.
Assuming that there are no 'leakages' from the credit multiplier circuit, i.e. that the private sector does not seek to convert part of the newly created book money into fiat money. The credit multiplier is the inverse of the reserve requirement ratio. ():
In the example: => . Si , .
There are several ways to demonstrate that . The simplest is to point out that . Or · . Therefore,
In general:
The Money Multiplier: full version[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
Exemple (Same same but different!)
1. Same assumption as above, that we abandon the assumption that agents in the non-bank sector do not seek to exchange some of the newly created book money for cash. In this case, when the bank makes a loan, it must expect that the cash-in-transaction money created in return will be exchanged for cash. This means that the bank will have to draw on its excess reserves to provide the requested cash. Excess reserves will decline more rapidly, because of this leakage out of the credit multiplier circuit, and the credit multiplier will therefore be lower.
Let us call the leakage coefficient, i.e. the share of new credits converted into cash:
2. Idem
3’. Bank A uses its excess reserves to make new loans (for an amount of 100). However, the non-bank sector wants to keep half of it in cash: Assumption: .
4’. The remaining excess reserves give rise to new loans for an amount of 40.
5’. The process can continue until there are no more excess reserves. The result is :
In its full version (with leakage), the credit multiplier becomes :
Evidence:
Because the process stops when mandatory stockpiling and leakage has exhausted the initial surplus reserves. Replacing the increase in reserve requirements and requests for conversion to cash with their respective values has:
- (car et )
- (car )
From then on:
BC's control instruments[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
Open market operations: as already mentioned, central banks can intervene in asset markets. When a CB buys (sells) government bonds the amount of money in circulation increases (decreases).
Modification of the reserve ratio: if the minimum fraction of deposits that must be kept as reserves increases (decrease), the quantity of money in circulation decreases (increases). NB: Traditionally, central banks have used this measure only very rarely, except in China in recent years. Examples: 10% USA, 20% CH, nothing UK, nothing Australia...
Change in the discount rate (or key rate): commercial banks borrow money from the central bank when their reserves are too low in relation to the reserve requirement. If the discount rate ↑ (↓) ⇒ the money supply ↓ (↑). Most central banks have lowered this rate since the beginning of the last financial crisis. Today the key rates are extremely low.
Effectiveness of the central bank's control of the money supply[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
Central banks exercise only partial control over the supply of money. In particular, central banks cannot control :
- the amount of deposits that households decide to convert into hard currency (leakage from the credit cycle). In this case, if private agents hold in cash a percentage of the deposits, the multiplier becomes , a good approximation of the true multiplier if and are small.
- the aggregate amount of loans made by commercial banks.
In summary, since the amount of money in circulation in the economy depends in part on the behaviour of bankers and depositors, central bank control can only be imperfect.
In the following we will assume that the central bank perfectly controls the supply of money.
Summary[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
The term money refers to all assets used by households to purchase goods and services.
Currency has three functions: exchange intermediary, unit of account, store of value, etc.
Commodity money is money that has an intrinsic value.
Currency has no intrinsic value.
The central bank controls the supply of money through open market operations by changing the reserve requirement ratio, changing the discount rate, etc.
The central bank cannot control the amount of loans granted by commercial banks or the deposit decisions of households. As a result, the central bank's control over the money supply is only partial.
Some causes of inflation (= increase in the general price level) are related to the determinants of the demand (next chapter) and supply (this chapter) of money.
Annexes[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
- David James Gill and Michael John Gill | The New Rules of Sovereign Debt | Foreignaffairs.com,. (2015). Retrieved 23 January 2015, from http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/142804/david-james-gill-and-michael-john-gill/the-great-ratings-game
References[modifier | modifier le wikicode]
- ↑ Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur le site de l'Université de Genève
- ↑ Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur le site de l'Université de Neuchâtel
- ↑ Page personnelle de Federica Sbergami sur Research Gate
- ↑ Researchgate.net - Nicolas Maystre
- ↑ Google Scholar - Nicolas Maystre
- ↑ VOX, CEPR Policy Portal - Nicolas Maystre
- ↑ Nicolas Maystre's webpage
- ↑ Cairn.info - Nicolas Maystre
- ↑ Linkedin - Nicolas Maystre
- ↑ Academia.edu - Nicolas Maystre









![{\displaystyle =100+80+64+51.2+...=100[1+(1-0.2)+(1-0.2)2+(1-0.2)3+...]=\lim _{n\to \infty }\sum _{i=0}^{n}100\times (1-0.2)^{i}={\frac {100}{1-(1-0.2)}}={\frac {100}{0.2}}=500}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9fd72fc4a1fc7a1105acd59867c384c23b9f1f47)
























![{\displaystyle =r[(1-c)\Delta CR]+c\Delta CR}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f4f72366cad05c9a6e6a8d2e7b6400ba75ab48c7)

![{\displaystyle =\Delta CR[c+r(1-c)]}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e33ca7ccc289e737b13639c4adc03da92f80bdef)



