« Political Behaviour: introductory course » : différence entre les versions
| Ligne 53 : | Ligne 53 : | ||
With regard to the concept of political behaviour, there is a broad definition, which is that political behaviour is all activities aimed at influencing the distribution of resources and power within a society. This includes aspects other than actions such as opinions, attitudes or beliefs. | With regard to the concept of political behaviour, there is a broad definition, which is that political behaviour is all activities aimed at influencing the distribution of resources and power within a society. This includes aspects other than actions such as opinions, attitudes or beliefs. | ||
== | ==Political participation== | ||
Milbrath | Milbrath proposes as a definition to characterize political participation which is "actions by private citizens through which they try to influence or support government and politics". There is both a notion of trying to have an effect on political elites, but there are also supporting activities. | ||
Other authors such as Verba exclude supportive activities while others exclude non-conventional participation. Others focus on the relational aspect with interactions between political authorities and citizens such as Barnes and Kaase. | |||
== | ==Voting behaviour== | ||
It is a participation that takes place in the context of elections, including free and competitive elections. This notion takes on meaning in democratic contexts. Voting behaviour is behaviour that is regulated and institutionalized by the state being more punctual and occurring at predefined times. | |||
In Switzerland, an important distinction must be made between voting and election. We will see, when we analyse the factors explaining these behaviours, that the factors are not always used to explain both types of behaviour. | |||
== | ==Three types of behaviour== | ||
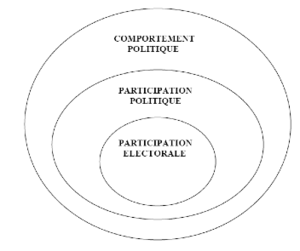
This graph summarizes the three types of political behaviour. Voter participation is one type of political participation and political participation is a subset of something broader that can be defined as political behaviour including, among other things, voting orientation. | |||
[[Fichier:comportement politique trois type de comportements 1.png|center|vignette|]] | [[Fichier:comportement politique trois type de comportements 1.png|center|vignette|]] | ||
==Action collective== | ==Action collective== | ||
It is a concept used in different fields in quite different ways. Collective action is group leadership that uses collective resources to defend common interests. A broad definition is that collective action is any action organized by more than two people. Narrower definitions emphasize that collective action is discontinuous and confrontational action, i.e., action that takes place in the context of social or political conflict. | |||
== | ==Protest Policy== | ||
In ''Dynamics of Contention'' publié en 2001, McAdam, Tarrow and Tilly define protest politics as a collective, episodic and public interaction between claimants and their objects. These authors have introduced other dimensions, namely that at least one government is involved in the claims as an author, object or party. If realized, the claims affect the interests of at least one of the claimants. We speak of collective action to the extent that if carried out, the collective action affects the interests of certain actors, not only the authors of the claims, but also the objects of the claims. For example, these are social movements, revolts, rebellions, terrorism, civil war or revolutions. | |||
== | ==Social movements== | ||
There is not really a consensus in the scientific literature. There is a substantialist definition which is that social movements are disadvantaged groups, i.e. groups that do not have access to institutional channels and mobilize to defend common interests through unconventional actions. A relational definition defines social movements as challenges to authorities based on common goals and shared social solidarities. | |||
== | ==Three types of non-conventional behaviour== | ||
[[Fichier:comportement politique trois type de comportements non conventionnels 1.png|center|vignette|]] | [[Fichier:comportement politique trois type de comportements non conventionnels 1.png|center|vignette|]] | ||
Version du 3 mai 2020 à 12:55
| Professeur(s) | Marco Giugni[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] |
|---|---|
| Cours | Comportement politique |
Lectures
- Introduction au cours de Comportement politique I
- Repères historiques et méthodologiques
- Les bases structurelles du comportement politique
- Les bases culturelles du comportement politique
- La socialisation politique
- L’acteur rationnel
- La participation politique
- Les modèles explicatifs du vote
- Les théories des mouvements sociaux
These are similar concepts that are related to the study of political behaviour or political behaviour because there is not only one type of political behaviour and several ways of behaving in politics :
- political participation/abstentionism ;
- political commitment;
- election/voting (voting behavior);
- opinion/attitude/values;
- political socialization: this is a key term and a concept at the heart of some explanations of voting behavior or social movements;
- public opinion;
- political parties/partisan competition;
- political institutions;
- interest in politics: it's a key concept;
- political competence: it's a concept operationalized somewhat differently by different authors;
- political sophistication: many theories emphasize that people who are more politically literate are more likely to participate.
- partisan identification: this is a central theory referring to the Michigan model;
- collective action/social movements;
- political influence: focuses on output behavior;
- decision-making processes;
- democracy.
Definition
Political behaviour
There are several definitions as for every concept in social sciences. Sometimes there is some consensus around a widely shared definition while for other concepts there is much less consensus and competition between different definitions. For electoral behaviour, there is a relatively broad consensus. On the other hand, for non-electoral behaviour, there is less consensus. These are two areas that have hardly ever spoken to each other. Attempts are being made to define the concepts that would apply to both areas.
With regard to the concept of political behaviour, there is a broad definition, which is that political behaviour is all activities aimed at influencing the distribution of resources and power within a society. This includes aspects other than actions such as opinions, attitudes or beliefs.
Political participation
Milbrath proposes as a definition to characterize political participation which is "actions by private citizens through which they try to influence or support government and politics". There is both a notion of trying to have an effect on political elites, but there are also supporting activities.
Other authors such as Verba exclude supportive activities while others exclude non-conventional participation. Others focus on the relational aspect with interactions between political authorities and citizens such as Barnes and Kaase.
Voting behaviour
It is a participation that takes place in the context of elections, including free and competitive elections. This notion takes on meaning in democratic contexts. Voting behaviour is behaviour that is regulated and institutionalized by the state being more punctual and occurring at predefined times.
In Switzerland, an important distinction must be made between voting and election. We will see, when we analyse the factors explaining these behaviours, that the factors are not always used to explain both types of behaviour.
Three types of behaviour
This graph summarizes the three types of political behaviour. Voter participation is one type of political participation and political participation is a subset of something broader that can be defined as political behaviour including, among other things, voting orientation.
Action collective
It is a concept used in different fields in quite different ways. Collective action is group leadership that uses collective resources to defend common interests. A broad definition is that collective action is any action organized by more than two people. Narrower definitions emphasize that collective action is discontinuous and confrontational action, i.e., action that takes place in the context of social or political conflict.
Protest Policy
In Dynamics of Contention publié en 2001, McAdam, Tarrow and Tilly define protest politics as a collective, episodic and public interaction between claimants and their objects. These authors have introduced other dimensions, namely that at least one government is involved in the claims as an author, object or party. If realized, the claims affect the interests of at least one of the claimants. We speak of collective action to the extent that if carried out, the collective action affects the interests of certain actors, not only the authors of the claims, but also the objects of the claims. For example, these are social movements, revolts, rebellions, terrorism, civil war or revolutions.
Social movements
There is not really a consensus in the scientific literature. There is a substantialist definition which is that social movements are disadvantaged groups, i.e. groups that do not have access to institutional channels and mobilize to defend common interests through unconventional actions. A relational definition defines social movements as challenges to authorities based on common goals and shared social solidarities.
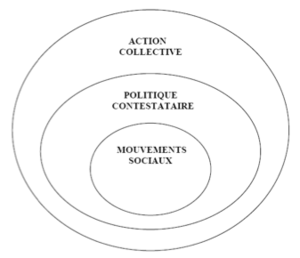
Three types of non-conventional behaviour
Le comportement politique dans les sciences sociales
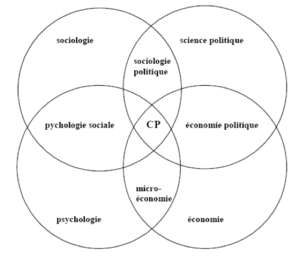
L’étude du comportement politique ne relève pas que de la science politique, mais peut être vue comme quelque chose transdisciplinaire notamment sociologique, sociopsychologique ou encore dans l’économie. Ces disciplines ensemble permettent d’éclairer l’étude des comportements politiques.
Le comportement politique peut être étudié sous différents angles. Il peut y avoir différentes approches notamment normative et prescriptive s’intéressant à ce que sont les bons comportements politiques. Il y a eu des théoriciens allant dans cette direction. Il s’agit d’essayer de faire ressortir les facteurs explicatifs permettant d’expliquer et de comprendre pourquoi les citoyens s’engagent en politique ou ne s’engagent pas, ou s’engagent dans certains types de comportements politiques. Avant, il faut poser un certain nombre de jalons conceptuels avec les différentes théories que cela soit les théories électorales ou non électorales.
Quelques questions
Toute réponse en sciences sociales et en science est une réponse provisoire :
- pourquoi certaines personnes vont voter et d’autres pas ?
- pourquoi les gens votent pour des partis différents ?
- pourquoi certaines personnes participent à des mouvements sociaux et d’autres pas ?
- quel est l’impact de l’origine sociale sur le comportement politique ?
- quel est l’impact des valeurs sur le comportement politique ?
- dans quelle mesure le comportement politique est-il rationnel ?
- dans quelle mesure le comportement politique est-il influencé par le contexte ?
- comment se sont transformées les modalités de la participation politique au fil du temps ?
Modèle de comportement politique
Ce que l’on veut identifier et expliquer est le comportement politique dans ses différentes formes et ce ou ces comportements politiques sont influencés par trois types de facteurs basés à des niveaux différents. Autant le contexte structurel que le contexte culturel jouent un rôle important au niveau macro. Au niveau méso se trouvent les réseaux sociaux dynamiques de groupe et in fine les choix et préférences des individus. L’idée est qu’il y a une imbrication de ces facteurs. Si on prend ces facteurs et qu’on les traite tous au niveau individuel, cela structure le cours parce que nous allons nous intéresser d’abord à la notion de clivage et sa traduction différente influençant le comportement politique.